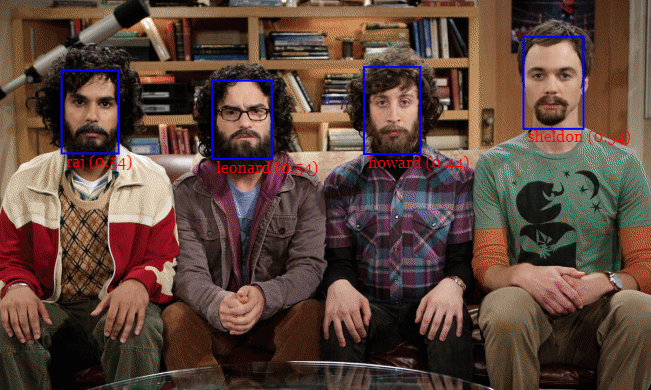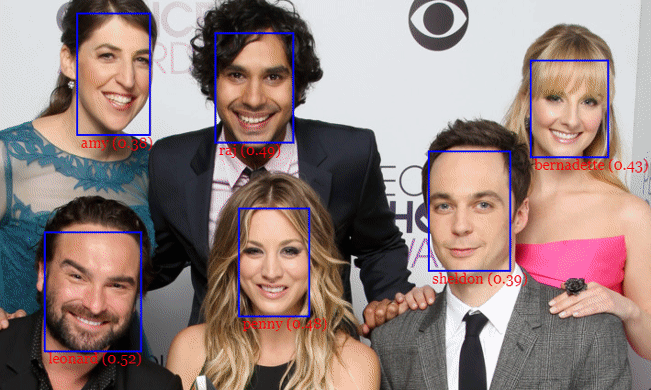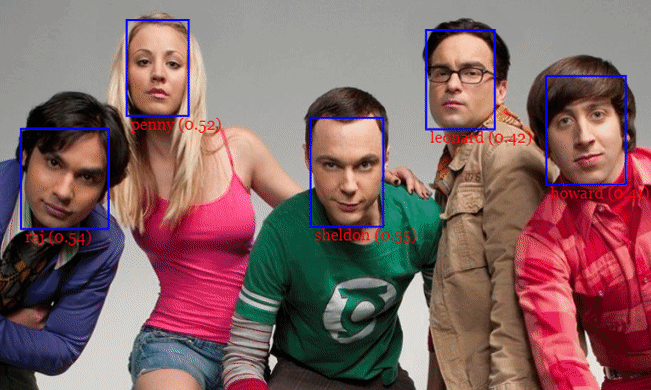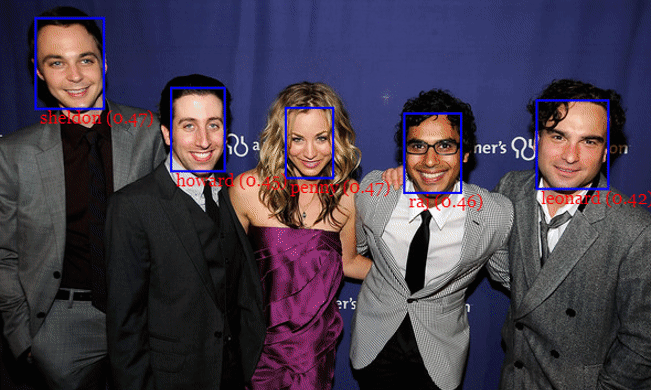
JavaScript API for face detection and face recognition in the browser implemented on top of the tensorflow.js core API (tensorflow/tfjs-core)
Check out my article face-api.js — JavaScript API for Face Recognition in the Browser with tensorflow.js for a quick introduction to the package.
SSD Mobilenet v1
MTCNN
cd examples
npm i
npm startBrowse to http://localhost:3000/.
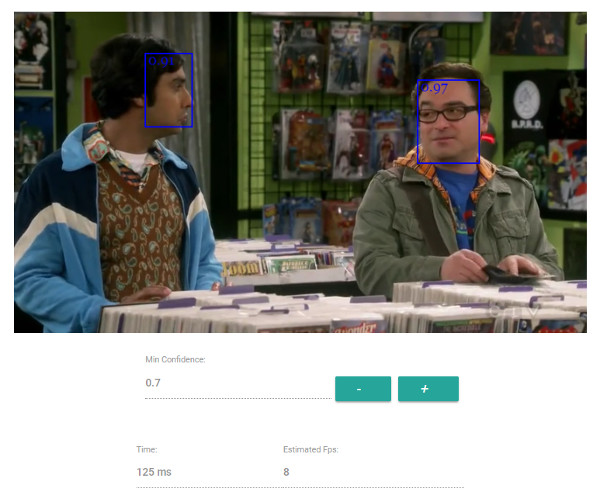
For face detection, this project implements a SSD (Single Shot Multibox Detector) based on MobileNetV1. The neural net will compute the locations of each face in an image and will return the bounding boxes together with it's probability for each face. This face detector is aiming towards obtaining high accuracy in detecting face bounding boxes instead of low inference time.
The face detection model has been trained on the WIDERFACE dataset and the weights are provided by yeephycho in this repo.
MTCNN (Multi-task Cascaded Convolutional Neural Networks) represents an alternative to SSD Mobilenet v1, which offers much more room for configuration and is able to achieve much lower processing times. MTCNN is a 3 stage cascaded CNN, which simultanously returns 5 face landmark points along with the bounding boxes and scores for each face. By limiting the minimum size of faces expected in an image, MTCNN allows you to process frames from your webcam in realtime. Additionally with 2MB, the size of the weights file is only a third of the size of the quantized SSD Mobilenet v1 model (~6MB).
MTCNN has been presented in the paper Joint Face Detection and Alignment using Multi-task Cascaded Convolutional Networks by Zhang et al. and the model weights are provided in the official repo of the MTCNN implementation.
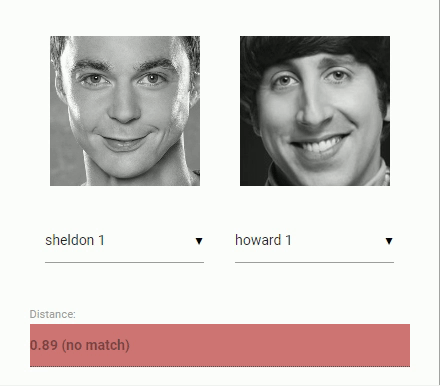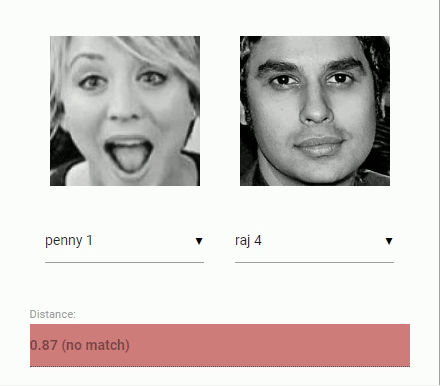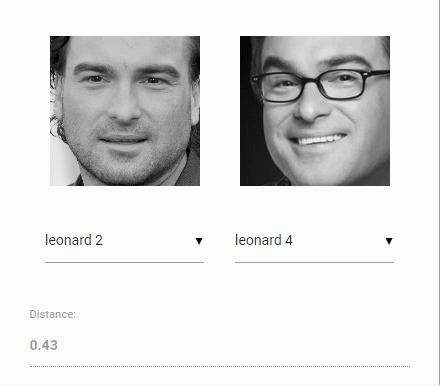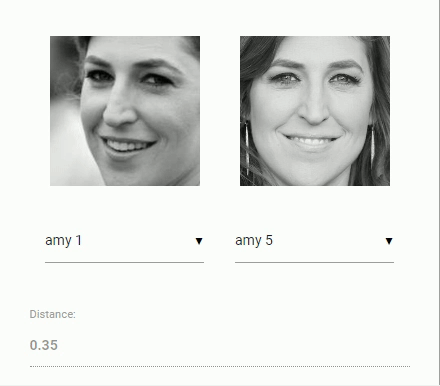
For face recognition, a ResNet-34 like architecture is implemented to compute a face descriptor (a feature vector with 128 values) from any given face image, which is used to describe the characteristics of a persons face. The model is not limited to the set of faces used for training, meaning you can use it for face recognition of any person, for example yourself. You can determine the similarity of two arbitrary faces by comparing their face descriptors, for example by computing the euclidean distance or using any other classifier of your choice.
The neural net is equivalent to the FaceRecognizerNet used in face-recognition.js and the net used in the dlib face recognition example. The weights have been trained by davisking and the model achieves a prediction accuracy of 99.38% on the LFW (Labeled Faces in the Wild) benchmark for face recognition.
This package implements a CNN to detect the 68 point face landmarks for a given face image.
The model has been trained on a variety of public datasets and the model weights are provided by yinguobing in this repo.
Get the latest build from dist/face-api.js or dist/face-api.min.js and include the script:
<script src="face-api.js"></script>Or install the package:
npm i face-api.jsTo load a model, you have provide the corresponding manifest.json file as well as the model weight files (shards) as assets. Simply copy them to your public or assets folder. The manifest.json and shard files of a model have to be located in the same directory / accessible under the same route.
Assuming the models reside in public/models:
await faceapi.loadFaceDetectionModel('/models')
// accordingly for the other models:
// await faceapi.loadFaceLandmarkModel('/models')
// await faceapi.loadFaceRecognitionModel('/models')
// await faceapi.loadMtcnnModel('/models')As an alternative, you can also create instance of the neural nets:
const net = new faceapi.FaceDetectionNet()
// accordingly for the other models:
// const net = new faceapi.FaceLandmarkNet()
// const net = new faceapi.FaceRecognitionNet()
// const net = new faceapi.Mtcnn()
await net.load('/models/face_detection_model-weights_manifest.json')
// await net.load('/models/face_landmark_68_model-weights_manifest.json')
// await net.load('/models/face_recognition_model-weights_manifest.json')
// await net.load('/models/mtcnn_model-weights_manifest.json')
// or simply load all models
await net.load('/models')Using instances, you can also load the weights as a Float32Array (in case you want to use the uncompressed models):
// using fetch
const res = await fetch('/models/face_detection_model.weights')
const weights = new Float32Array(await res.arrayBuffer())
net.load(weights)
// using axios
const res = await axios.get('/models/face_detection_model.weights', { responseType: 'arraybuffer' })
const weights = new Float32Array(res.data)
net.load(weights)Detect faces and get the bounding boxes and scores:
// optional arguments
const minConfidence = 0.8
const maxResults = 10
// inputs can be html canvas, img or video element or their ids ...
const myImg = document.getElementById('myImg')
const detections = await faceapi.locateFaces(myImg, minConfidence, maxResults)Draw the detected faces to a canvas:
// resize the detected boxes in case your displayed image has a different size then the original
const detectionsForSize = detections.map(det => det.forSize(myImg.width, myImg.height))
const canvas = document.getElementById('overlay')
canvas.width = myImg.width
canvas.height = myImg.height
faceapi.drawDetection(canvas, detectionsForSize, { withScore: false })You can also obtain the tensors of the unfiltered bounding boxes and scores for each image in the batch (tensors have to be disposed manually):
const { boxes, scores } = await net.forward('myImg')Detect faces and get the bounding boxes and scores:
// defaults parameters shown:
const forwardParams = {
// number of scaled versions of the input image passed through the CNN
// of the first stage, lower numbers will result in lower inference time,
// but will also be less accurate
maxNumScales: 10,
// scale factor used to calculate the scale steps of the image
// pyramid used in stage 1
scaleFactor: 0.709,
// the score threshold values used to filter the bounding
// boxes of stage 1, 2 and 3
scoreThresholds: [0.6, 0.7, 0.7],
// mininum face size to expect, the higher the faster processing will be,
// but smaller faces won't be detected
minFaceSize: 20
}
const results = await faceapi.mtcnn(document.getElementById('myImg'), forwardParams)Alternatively you can also specify the scale steps manually:
const forwardParams = {
scaleSteps: [0.4, 0.2, 0.1, 0.05]
}
const results = await faceapi.mtcnn(document.getElementById('myImg'), forwardParams)Finally you can draw the returned bounding boxes and 5 Point Face Landmarks into a canvas:
const minConfidence = 0.9
if (results) {
results.forEach(({ faceDetection, faceLandmarks }) => {
// ignore results with low confidence score
if (faceDetection.score < minConfidence) {
return
}
faceapi.drawDetection('overlay', faceDetection)
faceapi.drawLandmarks('overlay', faceLandmarks)
})
}Compute and compare the descriptors of two face images:
// inputs can be html canvas, img or video element or their ids ...
const descriptor1 = await faceapi.computeFaceDescriptor('myImg')
const descriptor2 = await faceapi.computeFaceDescriptor(document.getElementById('myCanvas'))
const distance = faceapi.euclideanDistance(descriptor1, descriptor2)
if (distance < 0.6)
console.log('match')
else
console.log('no match')Or simply obtain the tensor (tensor has to be disposed manually):
const t = await net.forward('myImg')Detect face landmarks:
// inputs can be html canvas, img or video element or their ids ...
const myImg = document.getElementById('myImg')
const landmarks = await faceapi.detectLandmarks(myImg)Draw the detected face landmarks to a canvas:
// adjust the landmark positions in case your displayed image has a different size then the original
const landmarksForSize = landmarks.forSize(myImg.width, myImg.height)
const canvas = document.getElementById('overlay')
canvas.width = myImg.width
canvas.height = myImg.height
faceapi.drawLandmarks(canvas, landmarksForSize, { drawLines: true })Retrieve the face landmark positions:
const landmarkPositions = landmarks.getPositions()
// or get the positions of individual contours
const jawOutline = landmarks.getJawOutline()
const nose = landmarks.getNose()
const mouth = landmarks.getMouth()
const leftEye = landmarks.getLeftEye()
const rightEye = landmarks.getRightEye()
const leftEyeBbrow = landmarks.getLeftEyeBrow()
const rightEyeBrow = landmarks.getRightEyeBrow()Compute the Face Landmarks for Detected Faces:
const detections = await faceapi.locateFaces(input)
// get the face tensors from the image (have to be disposed manually)
const faceTensors = await faceapi.extractFaceTensors(input, detections)
const landmarksByFace = await Promise.all(faceTensors.map(t => faceapi.detectLandmarks(t)))
// free memory for face image tensors after we computed their descriptors
faceTensors.forEach(t => t.dispose())After face detection has been performed, I would recommend to align the bounding boxes of the detected faces before passing them to the face recognition net, which will make the computed face descriptor much more accurate. Fortunately, the api can do this for you under the hood. You can obtain the full face descriptions (location, landmarks and descriptor) of each face in an input image as follows:
const fullFaceDescriptions = await faceapi.allFaces(input, minConfidence)
const fullFaceDescription0 = fullFaceDescriptions[0]
console.log(fullFaceDescription0.detection) // bounding box & score
console.log(fullFaceDescription0.landmarks) // 68 point face landmarks
console.log(fullFaceDescription0.descriptor) // face descriptorYou can also do everything manually as shown in the following:
// first detect the face locations
const detections = await faceapi.locateFaces(input, minConfidence)
// get the face tensors from the image (have to be disposed manually)
const faceTensors = (await faceapi.extractFaceTensors(input, detections))
// detect landmarks and get the aligned face image bounding boxes
const alignedFaceBoxes = await Promise.all(faceTensors.map(
async (faceTensor, i) => {
const faceLandmarks = await faceapi.detectLandmarks(faceTensor)
return faceLandmarks.align(detections[i])
}
))
// free memory for face image tensors after we detected the face landmarks
faceTensors.forEach(t => t.dispose())
// get the face tensors for the aligned face images from the image (have to be disposed manually)
const alignedFaceTensors = (await faceapi.extractFaceTensors(input, alignedFaceBoxes))
// compute the face descriptors from the aligned face images
const descriptors = await Promise.all(alignedFaceTensors.map(
faceTensor => faceapi.computeFaceDescriptor(faceTensor)
))
// free memory for face image tensors after we computed their descriptors
alignedFaceTensors.forEach(t => t.dispose())