| layout | title | parent | nav_order |
|---|---|---|---|
default |
Objects and Classes |
Oops Concept |
3 |
What is an object in Java object in Java
An entity that has state and behavior is known as an object e.g., chair, bike, marker, pen, table, car, etc. It can be physical or logical (tangible and intangible). The example of an intangible object is the banking system.
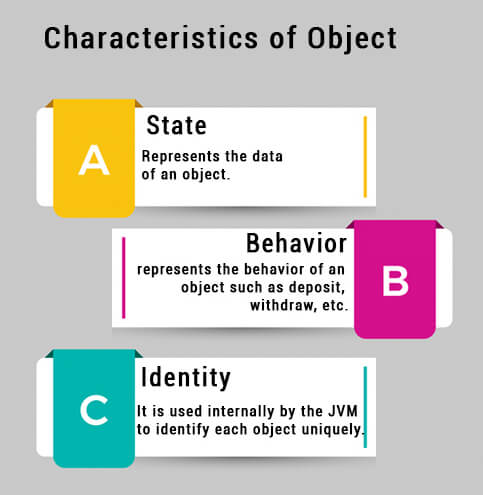
An object has three characteristics:
- State: represents the data (value) of an object.
- Behavior: represents the behavior (functionality) of an object such as deposit, withdraw, etc.
- Identity: An object identity is typically implemented via a unique ID. The value of the ID is not visible to the external user. However, it is used internally by the JVM to identify each object uniquely.
For Example, Pen is an object. Its name is Reynolds; color is white, known as its state. It is used to write, so writing is its behavior.
An object is an instance of a class. A class is a template or blueprint from which objects are created. So, an object is the instance(result) of a class.
Object Definitions:
- An object is a real-world entity.
- An object is a runtime entity.
- The object is an entity which has state and behavior.
- The object is an instance of a class.
A class is a group of objects which have common properties. It is a template or blueprint from which objects are created. It is a logical entity. It can't be physical.
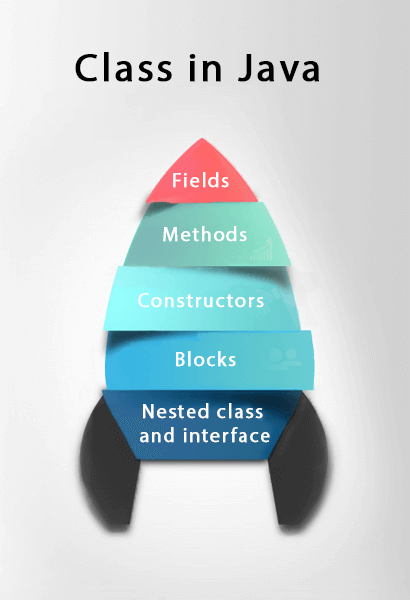
A class in Java can contain:
- Fields
- Methods
- Constructors
- Blocks
- Nested class and interface
Example code
class Student{
//defining fields
int id;//field or data member or instance variable
String name;
//creating main method inside the Student class
public static void main(String args[]){
//Creating an object or instance
Student s1=new Student();//creating an object of Student
//Printing values of the object
System.out.println(s1.id);//accessing member through reference variable
System.out.println(s1.name);
}
} Output
0
null