| layout | title | parent | nav_order |
|---|---|---|---|
default |
OOPs |
Oops Concept |
1 |
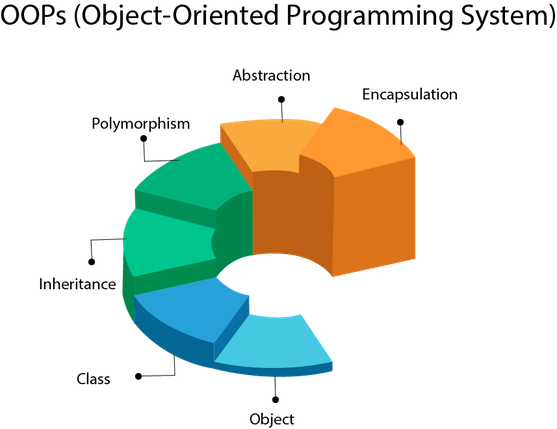
OOPs (Object-Oriented Programming System)
Object means a real-world entity such as a pen, chair, table, computer, watch, etc. Object-Oriented Programming is a methodology or paradigm to design a program using classes and objects. It simplifies software development and maintenance by providing some concepts:
Object
Class
Inheritance
Polymorphism
Abstraction
Encapsulation
Apart from these concepts, there are some other terms which are used in Object-Oriented design:
- Coupling
- Cohesion
- Association
- Aggregation
- Composition
Any entity that has state and behavior is known as an object. For example, a chair, pen, table, keyboard, bike, etc. It can be physical or logical.
An Object can be defined as an instance of a class. An object contains an address and takes up some space in memory. Objects can communicate without knowing the details of each other's data or code. The only necessary thing is the type of message accepted and the type of response returned by the objects.
Example: A dog is an object because it has states like color, name, breed, etc. as well as behaviors like wagging the tail, barking, eating, etc.
Collection of objects is called class. It is a logical entity.
A class can also be defined as a blueprint from which you can create an individual object. Class doesn't consume any space.
When one object acquires all the properties and behaviors of a parent object, it is known as inheritance. It provides code reusability. It is used to achieve runtime polymorphism.
If one task is performed in different ways, it is known as polymorphism. For example: to convince the customer differently, to draw something, for example, shape, triangle, rectangle, etc.
In Java, we use method overloading and method overriding to achieve polymorphism.
Another example can be to speak something; for example, a cat speaks meow, dog barks woof, etc.
Hiding internal details and showing functionality is known as abstraction. For example phone call, we don't know the internal processing.
In Java, we use abstract class and interface to achieve abstraction.
Binding (or wrapping) code and data together into a single unit are known as encapsulation. For example, a capsule, it is wrapped with different medicines.
A java class is the example of encapsulation. Java bean is the fully encapsulated class because all the data members are private here.