MIVisionX samples using OpenVX and OpenVX extensions. In the samples below we will learn how to run computer vision, inference, and a combination of computer vision & inference efficiently on target hardware.
- C/C++ Samples for OpenVX and OpenVX Extensions
- GDF - Graph Description Format Samples
- Loom 360 Stitch - Radeon Loom 360 Stitch Samples
- Model Compiler Samples - Run Efficient Inference
- MIVisionX Inference Deploy Samples
MIVisionX samples using RunVX
Note:
- To run the samples we need to put MIVisionX executables and libraries into the system path
export PATH=$PATH:/opt/rocm/bin
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=$LD_LIBRARY_PATH:/opt/rocm/lib
- To get help on RunVX, use
-hoption
runvx -h
usage:
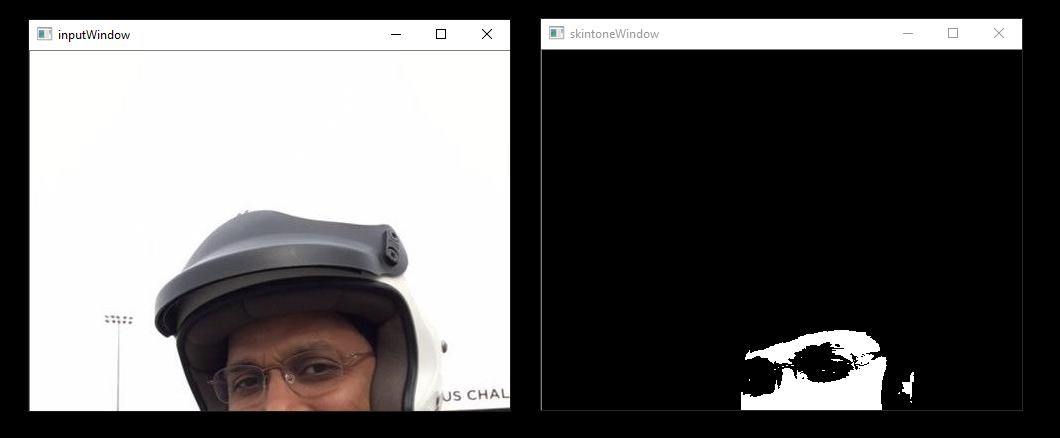
runvx gdf/skintonedetect.gdf
usage:
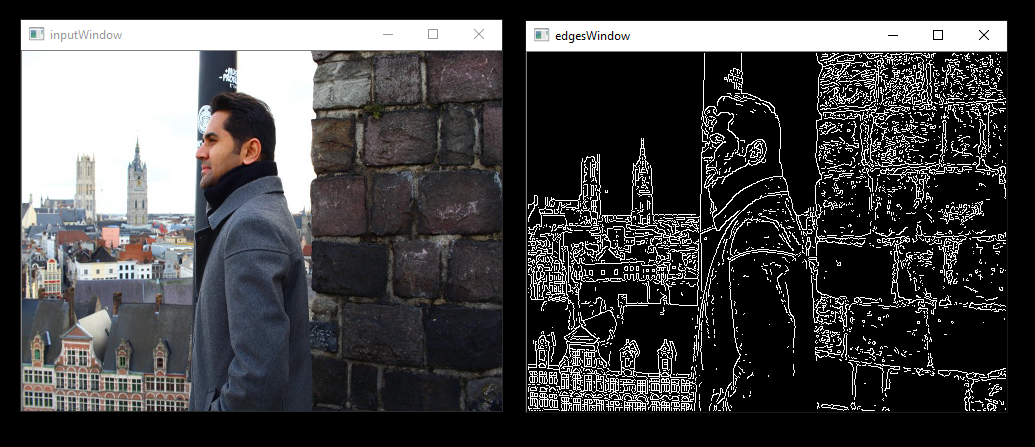
runvx gdf/canny.gdf
Using a live camera
usage:
runvx -frames:live gdf/skintonedetect-LIVE.gdf
Using a live camera
usage:
runvx -frames:live gdf/canny-LIVE.gdf
Using a live camera
usage:
runvx -frames:live gdf/OpenCV_orb-LIVE.gdf
MIVisionX samples in C/C++
usage:
cd c_samples/canny/
cmake .
make
./cannyDetect --image <imageName>
./cannyDetect --live
usage:
cd c_samples/opencv_orb/
cmake .
make
./orbDetect
MIVisionX samples using LoomShell
Note:
- To run the samples we need to put MIVisionX executables and libraries into the system path
export PATH=$PATH:/opt/rocm/bin
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=$LD_LIBRARY_PATH:/opt/rocm/lib
- To get help on loom_shell, use
-helpoption
loom_shell -help
usage:
- Get Data for the stitch
cd loom_360_stitch/sample-1/
python loomStitch-sample1-get-data.py
- Run Loom Shell Script to generate the 360 Image
loom_shell loomStitch-sample1.txt
- Expected Output
loom_shell loomStitch-sample1.txt
loom_shell 0.9.8 [loomsl 0.9.8]
... processing commands from loomStitch-sample1.txt
..ls_context context[1] created
..lsCreateContext: created context context[0]
..lsSetOutputConfig: successful for context[0]
..lsSetCameraConfig: successful for context[0]
OK: OpenVX using GPU device#0 (gfx906+sram-ecc) [OpenCL 2.0 ] [SvmCaps 0 0]
..lsInitialize: successful for context[0] (1380.383 ms)
..cl_mem mem[2] created
..cl_context opencl_context[1] created
..lsGetOpenCLContext: get OpenCL context opencl_context[0] from context[0]
OK: loaded cam00.bmp
OK: loaded cam01.bmp
OK: loaded cam02.bmp
OK: loaded cam03.bmp
..lsSetCameraBuffer: set OpenCL buffer mem[0] for context[0]
..lsSetOutputBuffer: set OpenCL buffer mem[1] for context[0]
OK: run: executed for 100 frames
OK: run: Time: 0.919 ms (min); 1.004 ms (avg); 1.238 ms (max); 1.212 ms (1st-frame) of 100 frames
OK: created LoomOutputStitch.bmp
> stitch graph profile
COUNT,tmp(ms),avg(ms),min(ms),max(ms),DEV,KERNEL
100, 0.965, 1.005, 0.918, 1.237,CPU,GRAPH
100, 0.959, 0.999, 0.915, 1.234,GPU,com.amd.loomsl.warp
100, 0.955, 0.994, 0.908, 1.232,GPU,com.amd.loomsl.merge
OK: OpenCL buffer usage: 324221600, 9/9
..lsReleaseContext: released context context[0]
... exit from loomStitch-sample1.txt
Note: The stitched output image is saved as LoomOutputStitch.bmp
usage:
- Get Data for the stitch
cd loom_360_stitch/sample-2/
python loomStitch-sample2-get-data.py
- Run Loom Shell Script to generate the 360 Image
loom_shell loomStitch-sample2.txt
usage:
- Get Data for the stitch
cd loom_360_stitch/sample-3/
python loomStitch-sample3-get-data.py
- Run Loom Shell Script to generate the 360 Image
loom_shell loomStitch-sample3.txt
In this sample, we will learn how to run inference efficiently using OpenVX and OpenVX Extensions. The sample will go over each step required to convert a pre-trained neural net model into an OpenVX Graph and run this graph efficiently on any target hardware. In this sample, we will also learn about AMD MIVisionX which delivers open-source implementation of OpenVX and OpenVX Extensions along with MIVisionX Neural Net Model Compiler & Optimizer.