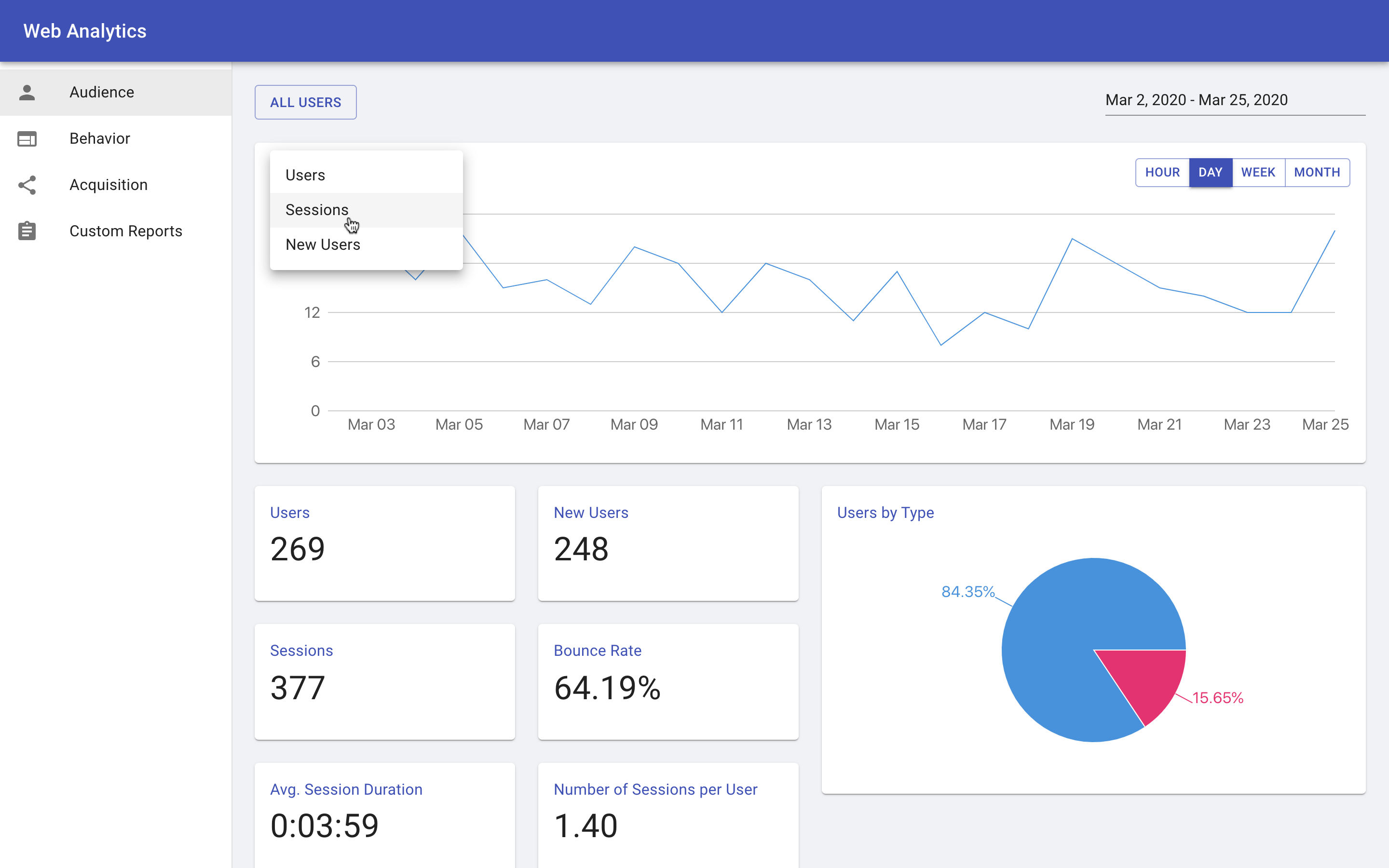
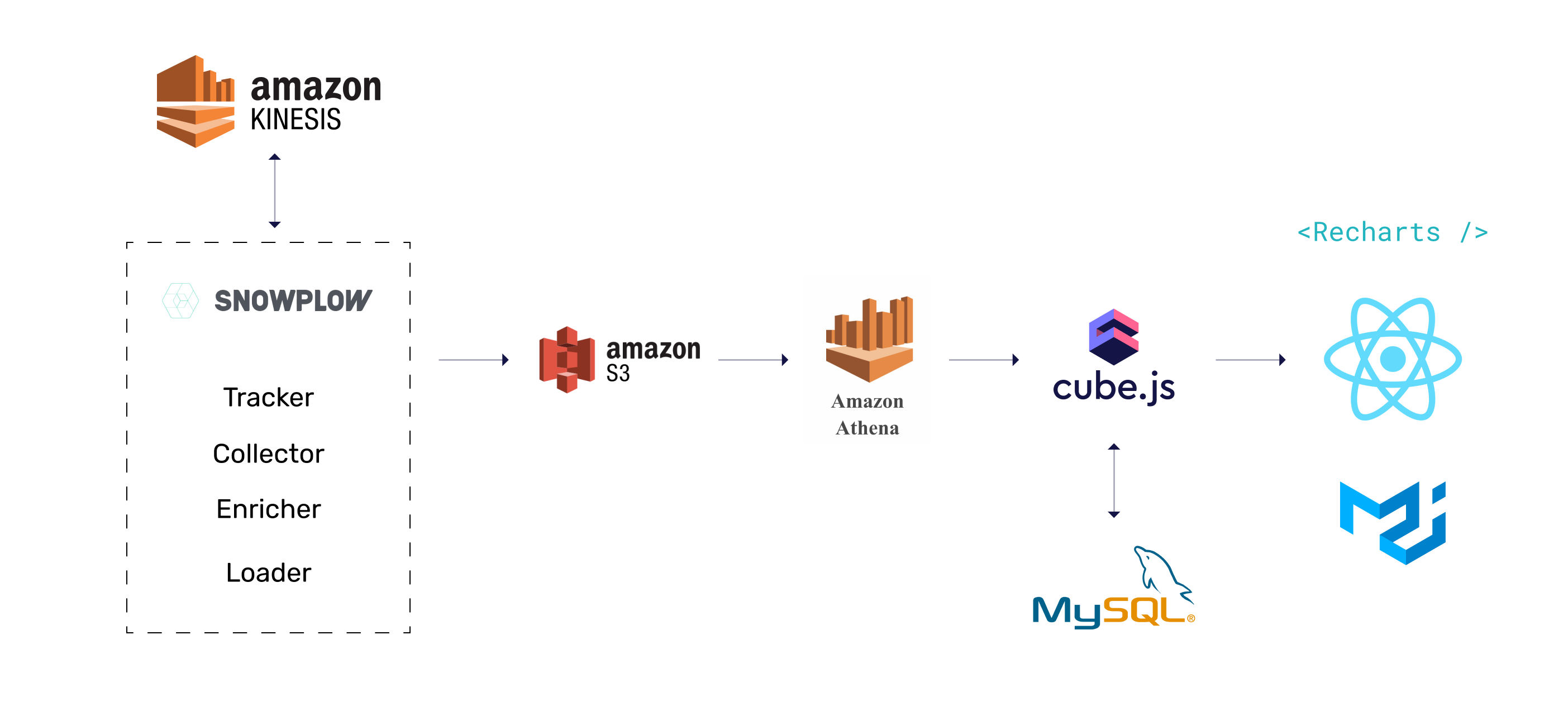
The example application uses Cube.js as the analytics backend, Snowplow for data collection, and Athena as the main data warehouse. The frontend is built with React, Material UI, and Recharts.
Online demo: web-analytics-demo.cubecloudapp.dev
Tutorial: Building an Open Source Web Analytics Platform
Ready-to-use. Follow the installation guide below to install the whole stack from data collection to the frontend application. It comes with all Cube.js schema definitions for sessionization and attribution, as well as configured pre-aggregations for optimal performance.
Hackable. Use this demo application as a starting point to create your own web analytics platform. It’s designed to be completely customizable on every level. You can switch to a different data collection engine or build your own, use any SQL database as a warehouse, change how metrics are defined, and completely customize the frontend.
Performance first. The response time is under 50 ms by using Cube.js pre-aggregations. It scales well for tracking up to several million daily active users. To achieve this performance, Cube.js stores and manages aggregated tables in MySQL with a 5-minute refresh rate. You can learn more about performance optimization with external pre-aggregations in this blog post.
Below you can find the architecture of the example application. It relies on some AWS services, which can be partially or fully substituted by open-source tools: Kafka, MinIO and PrestoDB instead of Kinesis, S3 and Athena respectively.
The data collection part is handled by Snowplow. Follow Snowplow’s Setup Guide to install the Tracker, Collector, Enrich, and S3 Loader.
Once you have data in the S3 the next step is to set up Athena or Presto to query it. We’ll describe only Athena with an S3 setup here, but you can easily find a lot of materials online on how to set up an alternative configuration.
To query S3 data with Athena, we need to create a table for Snowplow events. Copy and paste the following DDL statement into the Athena console. Modify the LOCATION for the S3 bucket that stores your enriched Snowplow events.
Show DDL statement
CREATE EXTERNAL TABLE atomic_events (
app_id STRING,
platform STRING,
etl_tstamp TIMESTAMP,
collector_tstamp TIMESTAMP,
dvce_tstamp TIMESTAMP,
event STRING,
event_id STRING,
txn_id INT,
name_tracker STRING,
v_tracker STRING,
v_collector STRING,
v_etl STRING,
user_id STRING,
user_ipaddress STRING,
user_fingerprint STRING,
domain_userid STRING,
domain_sessionidx INT,
network_userid STRING,
geo_country STRING,
geo_region STRING,
geo_city STRING,
geo_zipcode STRING,
geo_latitude STRING,
geo_longitude STRING,
geo_region_name STRING,
ip_isp STRING,
ip_organization STRING,
ip_domain STRING,
ip_netspeed STRING,
page_url STRING,
page_title STRING,
page_referrer STRING,
page_urlscheme STRING,
page_urlhost STRING,
page_urlport INT,
page_urlpath STRING,
page_urlquery STRING,
page_urlfragment STRING,
refr_urlscheme STRING,
refr_urlhost STRING,
refr_urlport INT,
refr_urlpath STRING,
refr_urlquery STRING,
refr_urlfragment STRING,
refr_medium STRING,
refr_source STRING,
refr_term STRING,
mkt_medium STRING,
mkt_source STRING,
mkt_term STRING,
mkt_content STRING,
mkt_campaign STRING,
contexts STRING,
se_category STRING,
se_action STRING,
se_label STRING,
se_property STRING,
se_value STRING,
unstruct_event STRING,
tr_orderid STRING,
tr_affiliation STRING,
tr_total STRING,
tr_tax STRING,
tr_shipping STRING,
tr_city STRING,
tr_state STRING,
tr_country STRING,
ti_orderid STRING,
ti_sku STRING,
ti_name STRING,
ti_category STRING,
ti_price STRING,
ti_quantity INT,
pp_xoffset_min INT,
pp_xoffset_max INT,
pp_yoffset_min INT,
pp_yoffset_max INT,
useragent STRING,
br_name STRING,
br_family STRING,
br_version STRING,
br_type STRING,
br_renderengine STRING,
br_lang STRING,
br_features_pdf STRING,
br_features_flash STRING,
br_features_java STRING,
br_features_director STRING,
br_features_quicktime STRING,
br_features_realplayer STRING,
br_features_windowsmedia STRING,
br_features_gears STRING,
br_features_silverlight STRING,
br_cookies STRING,
br_colordepth STRING,
br_viewwidth INT,
br_viewheight INT,
os_name STRING,
os_family STRING,
os_manufacturer STRING,
os_timezone STRING,
dvce_type STRING,
dvce_ismobile STRING,
dvce_screenwidth INT,
dvce_screenheight INT,
doc_charset STRING,
doc_width INT,
doc_height INT,
tr_currency STRING,
tr_total_base STRING,
tr_tax_base STRING,
tr_shipping_base STRING,
ti_currency STRING,
ti_price_base STRING,
base_currency STRING,
geo_timezone STRING,
mkt_clickid STRING,
mkt_network STRING,
etl_tags STRING,
dvce_sent_tstamp TIMESTAMP,
refr_domain_userid STRING,
refr_dvce_tstamp TIMESTAMP,
derived_contexts STRING,
domain_sessionid STRING,
derived_tstamp TIMESTAMP
)
PARTITIONED BY(run STRING)
ROW FORMAT DELIMITED
FIELDS TERMINATED BY '\\t'
STORED AS TEXTFILE
LOCATION 's3://bucket-name/path/to/enriched/good';This template uses MySQL as an external pre-aggregations database for performance optimization. Cube.js builds pre-aggregations from data stored in the main data warehouse, Athena in this example, and then uploads them into MySQL. Cube.js handles the refresh and partitioning of the pre-aggregations as well. You need to install MySQL and let Cube.js to connect to it. You can learn more about external pre-aggregations in the documentation here.
First, you need to download or clone the code inside examples/web-analytics
folder and install all the dependencies by running the following command:
$ npm installThe next step is to set environment variables required to run Cube.js backend.
You can use .env file to store your credentials or provide them in any other way
you'd prefer. Here the list of env variables you need to provide -
CUBEJS_AWS_REGION=Your Athena region (e.g. us-east-1)
CUBEJS_AWS_S3_OUTPUT_LOCATION=Your S3 Output location
# You can find the Athena S3 Output location here: https://docs.aws.amazon.com/athena/latest/ug/querying.html
CUBEJS_JDBC_DRIVER=athena
CUBEJS_DB_TYPE=athena
CUBEJS_API_SECRET=SECRET-SECURE-STRING
CUBEJS_EXT_DB_HOST=Your MySQL host
CUBEJS_EXT_DB_NAME=Table name for pre-aggregations (e.g. cubejs_pre_aggregations)
CUBEJS_EXT_DB_USER=MySQL username
CUBEJS_EXT_DB_PASS=Password for MySQl user
Now, you can run the Cube.js server with the following command:
$ npm startIt will start the Cube.js server on http://localhost:4000. By default, it starts in the development environment and serves Cube.js
Playground on the root route. To start the frontend app in the development you can navigate
into dashboard-app folder, install dependencies, and run yarn start.
It will start serving the frontend app from http://localhost:3000.
To run it in the production mode you need first to build the frontend. To do that navigate into
dashboard-app folder, install dependencies, and run
yarn build. Then start the Cube.js server in the production mode by setting NODE_ENV=production env variable.
It will serve the frontend app on the root route in the production mode.
For deployment, you can easily build a docker image from the provided Dockerfile.
You can enable authentication to let only users with emails with specific domains to sign in. To enable it, you need to define the following environment variables -
GOOGLE_AUTH_DOMAIN=DOMAIN-TO-ALLOW-SIGN-INS-FROM
GOOGLE_AUTH_REDIRECT=URL-OF-YOUR-DEPLOYMENT (e.g.: <https://analytics.myapp.com>)
GOOGLE_AUTH_CLIENT_ID=GOOGLE_CLIENT_ID
GOOGLE_AUTH_CLIENT_SECRET=GOOGLE_CLIENT_SECRETTo obtain GOOGLE_CLIENT_ID and GOOGLE_CLIENT_SECRET you must register an application with Google. If you have not already done so, a new project can be created in the Google Developers Console. Your application will be issued a client ID and client secret. You will also need to configure a redirect URI, which should match the following pattern - GOOGLE_AUTH_REDIRECT/auth/google/callback, where GOOGLE_AUTH_REDIRECT is an environment variable you defined before.
Template uses Apollo GraphQL for CRUD operations related to custom reports. It uses localStorage currently for persistence. You can update GraphQL queries and mutations, as well as Apollo client configurations to use your GraphQL backend for persistent storage of custom reports.