diff --git a/_partials/_high-availability-setup.md b/_partials/_high-availability-setup.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..466ab1b8c9
--- /dev/null
+++ b/_partials/_high-availability-setup.md
@@ -0,0 +1,16 @@
+
+
+1. In [Timescale Console][cloud-login], select the service to enable replication for.
+1. Click `Operations`, then select `High availability`.
+1. Choose your replication strategy, then click `Change configuration`.
+ 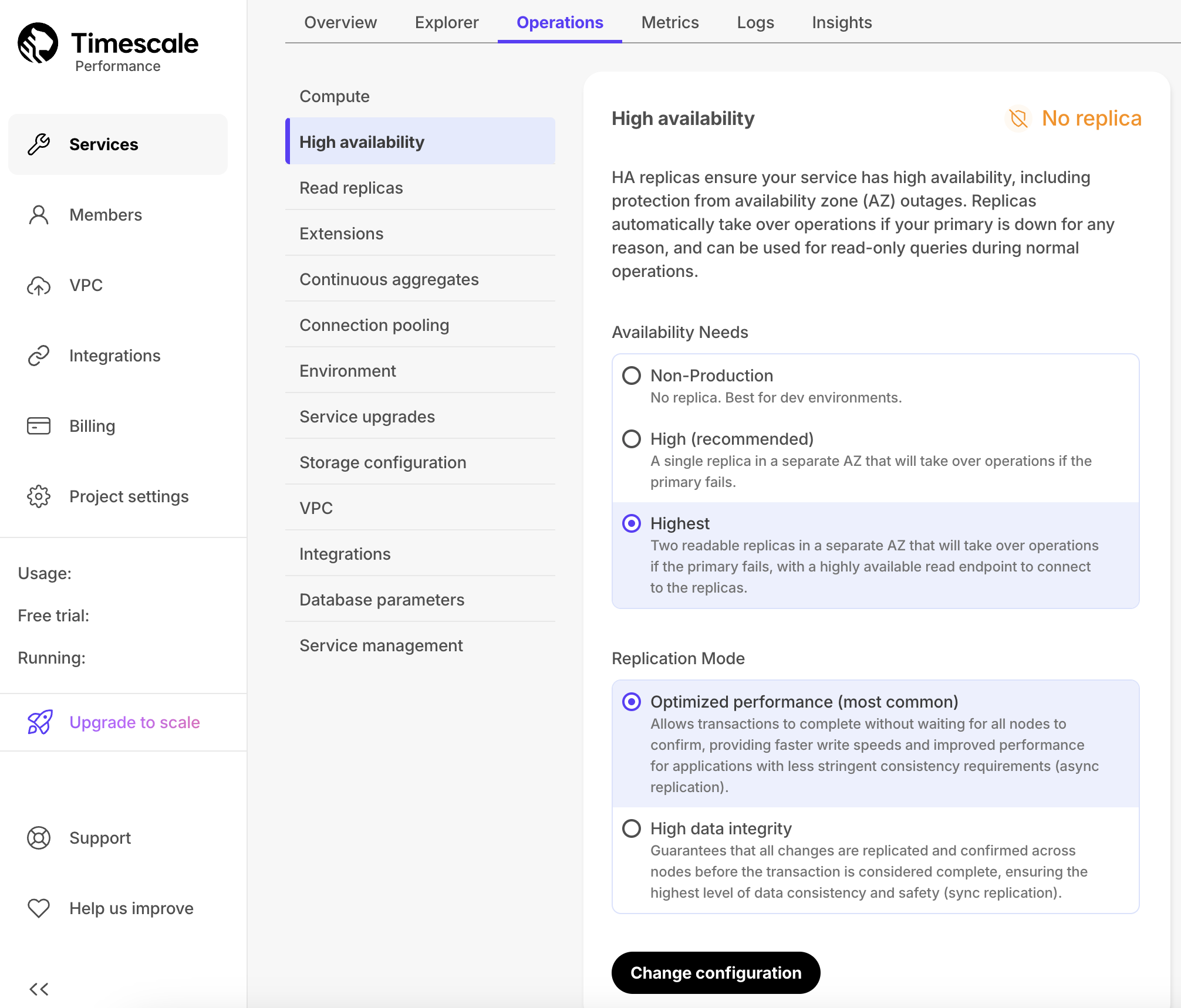 +
+1. In `Change high availability configuration`, click `Change config`.
+
+
+
+[cloud-login]: https://console.cloud.timescale.com
diff --git a/_partials/_where-to-next.md b/_partials/_where-to-next.md
index 5d1124a297..e7501f1d62 100644
--- a/_partials/_where-to-next.md
+++ b/_partials/_where-to-next.md
@@ -1,7 +1,11 @@
-Now you have TimescaleDB running, have a look at the:
+What next? [Try the main features offered by Timescale][try-timescale-features], see the [use case tutorials][tutorials],
+interact with the data in your $SERVICE_LONG using [your favorite programming language][connect-with-code], integrate
+your $SERVICE_LONG with a range of [third-party tools][integrations], plain old [Use Timescale][use-timescale], or dive
+into [the API][use-the-api].
-* [Tutorials][tutorials]: walk through a variety of business scenarios using example datasets.
-* [Use Timescale][tsdb-docs]: browse the features available with TimescaleDB.
-
-[tsdb-docs]: /use-timescale/:currentVersion:/
[tutorials]: /tutorials/:currentVersion:/
+[connect-with-code]: /quick-start/:currentVersion:/
+[integrations]: /use-timescale/:currentVersion:/integrations/
+[use-the-api]: /api/:currentVersion:/
+[use-timescale]: /use-timescale/:currentVersion:/
+[try-timescale-features]: /getting-started/:currentVersion:/test-drive-timescale-features/
diff --git a/getting-started/index.md b/getting-started/index.md
index 8fe5d5f27a..1b1bc30aae 100644
--- a/getting-started/index.md
+++ b/getting-started/index.md
@@ -16,21 +16,28 @@ import WhereNext from "versionContent/_partials/_where-to-next.mdx";
This section shows you how to:
-1. [Create and connect to a Timescale service][services-create]
-1. [Run queries from Timescale Console][run-queries-from-console]
-1. [Ingest some real financial data into your database][ingest-data]
-1. [Construct some interesting queries][queries] Try out some live queries
-1. [Create and query a continuous aggregates][caggs]
+1. [Create and connect to a $SERVICE_LONG][services-create]: choose the capabilities that match your business and
+ engineering needs on $COMPANY's cloud-based PostgreSQL platform.
+1. [Run queries from $CONSOLE][run-queries-from-console]: securely interact your data in the $CONSOLE UI.
+1. [Try the main features in Timescale products][test-drive]: rapidly implement the features in $CLOUD_LONG that
+ enable you to ingest and query data faster while keeping prices low.
-Already know the basics? See the
-[more advanced tutorials][tutorials], or see how to
-[Use Timescale][use-timescale].
+What next? See the [use case tutorials][tutorials], interact with the data in your $SERVICE_LONG using
+[your favorite programming language][connect-with-code], integrate your $SERVICE_LONG with a range of
+[third-party tools][integrations], plain old [Use Timescale][use-timescale], or dive into [the API][use-the-api].
[tutorials]: /tutorials/:currentVersion:/
+[connect-with-code]: /quick-start/:currentVersion:/
+[integrations]: /use-timescale/:currentVersion:/integrations/
+[use-the-api]: /api/:currentVersion:/
[use-timescale]: /use-timescale/:currentVersion:/
+
+
[services-create]: /getting-started/:currentVersion:/services#create-your-timescale-account
[services-connect]: /getting-started/:currentVersion:/services/#connect-to-your-service
+[test-drive]: /getting-started/:currentVersion:/test-drive-timescale-features/
[run-queries-from-console]: /getting-started/:currentVersion:/run-queries-from-console/
[ingest-data]: /getting-started/:currentVersion:/time-series-data/
[queries]: /getting-started/:currentVersion:/queries/
[caggs]: /getting-started/:currentVersion:/aggregation/
+
diff --git a/getting-started/page-index/page-index.js b/getting-started/page-index/page-index.js
index ef51f973f8..17645679ae 100644
--- a/getting-started/page-index/page-index.js
+++ b/getting-started/page-index/page-index.js
@@ -15,29 +15,9 @@ module.exports = [
excerpt: "Run your queries securely from inside Timescale Console",
},
{
- title: "Tables and hypertables",
- href: "tables-hypertables",
- excerpt: "Create tables and hypertables for your data",
- },
- {
- title: "Time-series data",
- href: "time-series-data",
- excerpt: "Add time-series data to your database",
- },
- {
- title: "Queries",
- href: "queries",
- excerpt: "Query your data using full SQL",
- },
- {
- title: "Aggregation",
- href: "aggregation",
- excerpt: "Query aggregated data, and create a continuous aggregate",
- },
- {
- title: "Next steps",
- href: "next-steps",
- excerpt: "Get even more from your Timescale database",
+ title: "Try the main features in Timescale products",
+ href: "test-drive-timescale-features",
+ excerpt: "Improve database performance with Hypertables, time bucketing, continuous aggregates, compression, data tiering, and high availability",
},
],
},
diff --git a/getting-started/run-queries-from-console.md b/getting-started/run-queries-from-console.md
index e200244f32..f2a8a2f868 100644
--- a/getting-started/run-queries-from-console.md
+++ b/getting-started/run-queries-from-console.md
@@ -6,6 +6,8 @@ layout_components: [next_prev_large]
content_group: Getting started
---
+import WhereNext from "versionContent/_partials/_where-to-next.mdx";
+
# Run your queries from Timescale Console
As Timescale Cloud is based on PostgreSQL, you can use lots of [different tools][integrations] to
@@ -225,6 +227,7 @@ To use SQL editor with Timescale:
details.
+
[readreplica]: /use-timescale/:currentVersion:/ha-replicas/read-scaling/
[run-popsql]: /getting-started/:currentVersion:/run-queries-from-console/#data-mode
diff --git a/getting-started/services.md b/getting-started/services.md
index 105f80f60f..cc0c0f1af4 100644
--- a/getting-started/services.md
+++ b/getting-started/services.md
@@ -11,6 +11,7 @@ import Connect from "versionContent/_partials/_cloud-connect.mdx";
import CreateAHypertable from "versionContent/_partials/_create-hypertable.mdx";
import ServiceOverview from "versionContent/_partials/_service-overview.mdx";
import CloudIntro from "versionContent/_partials/_cloud-intro.mdx";
+import WhereNext from "versionContent/_partials/_where-to-next.mdx";
# Create your first $SERVICE_LONG
@@ -59,11 +60,10 @@ A Timescale service comes with access control to its data. To be able to run que
-## Create a hypertable
+And that is it, you are up and running. Enjoy developing with $COMPANY.
-
+
-And that is it, you are up and running. Enjoy developing with $COMPANY.
[tsc-portal]: https://console.cloud.timescale.com/
[services-how-to]: /use-timescale/:currentVersion:/services/
diff --git a/getting-started/test-drive-timescale-features.md b/getting-started/test-drive-timescale-features.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..ad5f015318
--- /dev/null
+++ b/getting-started/test-drive-timescale-features.md
@@ -0,0 +1,344 @@
+---
+title: Try the main features in Timescale products
+excerpt: Improve database performance with hypertables, time bucketing, compression and continuous aggregates.
+products: [cloud]
+content_group: Getting started
+---
+
+import HASetup from 'versionContent/_partials/_high-availability-setup.mdx';
+
+# Try the main features in Timescale products
+
+$CLOUD_LONG scales PostgreSQL to ingest and query vast amounts of live data. $CLOUD_LONG
+provides a range of features and optimizations that supercharge your queries while keeping the
+costs down. For example:
+* The row-columnar engine makes queries up to 350x faster, ingests 44% faster, and reduces storage by 95%.
+* Tiered storage seamlessly moves your data from high performance storage for frequently access data to low cost bottomless storage for rarely accessed data.
+
+You use the same optimization methods for data in all storage tiers:
+
+
+
+This page gives shows you how to rapidly implement the features in $CLOUD_LONG that enable you to
+ingest and query data faster while keeping prices low.
+
+## Prerequisites
+
+To run the examples in this page, you need either:
+- A [$SERVICE_LONG][create-a-service] with time-series and ai and vector capabilities enabled.
+- A [self-hosted PostgreSQL deployment][deploy-self-hosted] with the TimescaleDB, pgvector, pgvectorscale and
+ pgai extensions enabled in your database.
+
+## Optimize time-series data in hypertables
+
+Hypertables are PostgreSQL tables that help you improve insert and query
+performance by automatically partition your data by time. Each hypertable is made
+up of child tables called chunks. Each chunk is assigned a range of time, and only
+contains data from that range. You can also tune hypertables to increase performance
+even more.
+
+Hypertables exist alongside regular PostgreSQL tables.
+You use regular PostgreSQL tables for relational data, and interact with hypertables
+and regular PostgreSQL tables in the same way.
+
+This section shows you how to create regular tables and hypertables, and import
+relational and time-series data from external files.
+
+
+
+1. **Import some time-series data into your hypertable**
+
+ 1. Unzip [real_time_stock_data.zip](https://assets.timescale.com/docs/downloads/get-started/real_time_stock_data.zip) to a ``.
+
+ This test dataset contains second-by-second stock-trade data for the top 100 most-traded symbols
+ and a regular table of company symbols and company names.
+
+ To import up to 100GB of data directly from your current PostgreSQL based database,
+ [migrate with downtime][migrate-with-downtime] using native PostgreSQL tooling. To seamlessly import 100GB-10TB+
+ of data, use the [live migration][migrate-live] tooling supplied by $COMPANY. To add data from non-PostgreSQL
+ data sources, see [Import and ingest data][data-ingest].
+
+ 1. Upload data from the CSV files to your $SERVICE_SHORT:
+
+
+
+
+
+ The $CONSOLE data upload creates the tables for you from the data you are uploading:
+ 1. In [$CONSOLE][portal-ops-mode], select the service to add data to, then click **Actions** > **Upload CSV**.
+ 1. Drag `/tutorial_sample_company.csv`.
+ 1. Change `New table name` to `company`, then click `Upload CSV`.
+ 1. Use the same process to upload `/tutorial_sample_tick.csv` to the `stocks_real_time` table.
+ 1. Convert the `stocks_real_time relational` relational table to a hypertable.
+
+ In $CONSOLE. click `SQL editor`, then run the following query:
+
+ ```sql
+ SELECT create_hypertable('stocks_real_time', by_range('time'), migrate_data => TRUE);
+ ```
+
+ To more fully understand how hypertables work, and how to optimize them for performance by
+ tuning chunk intervals and enabling chunk skipping, see [the hypertables documentation][hypertables-section].
+
+
+
+
+
+ 1. In Terminal, navigate to `` and connect to your $SERVICE_SHORT.
+ ```bash
+ psql -d "postgres://:@:/"
+ ```
+ The connection information for a $SERVICE_SHORT is available in the file you downloaded when you created it.
+
+ 2. Create tables for the data to import
+
+ - For the time-series data:
+ 1. In your sql client, create a normal PostgreSQL table:
+
+ ```sql
+ CREATE TABLE stocks_real_time (
+ time TIMESTAMPTZ NOT NULL,
+ symbol TEXT NOT NULL,
+ price DOUBLE PRECISION NULL,
+ day_volume INT NULL
+ );
+ ```
+ 1. Convert `stocks_real_time` to a hypertable:
+ ```sql
+ SELECT create_hypertable('stocks_real_time', by_range('time'));
+ ```
+ To more fully understand how hypertables work, and how to optimize them for performance by
+ tuning chunk intervals and enabling chunk skipping, see [the hypertables documentation][hypertables-section].
+
+ - For the relational data:
+
+ In your sql client, create a normal PostgreSQL table:
+ ```sql
+ CREATE TABLE company (
+ symbol TEXT NOT NULL,
+ name TEXT NOT NULL
+ );
+ ```
+
+ 3. Upload the dataset to your $SERVICE_SHORT
+ ```sql
+ \COPY stocks_real_time from './tutorial_sample_tick.csv' DELIMITER ',' CSV HEADER;
+ \COPY company from './tutorial_sample_company.csv' DELIMITER ',' CSV HEADER;
+ ```
+
+
+
+
+
+1. **Have a quick look at your data**
+
+ You query hypertables in exactly the same way as you would a relational PostgreSQL table.
+ Use one of the following SQL editors to run a query and see the data you uploaded:
+ - **Data mode**: write queries, visualize data, and share your results in [$CONSOLE][portal-data-mode] for all your $SERVICE_LONGs.
+ - **SQL editor**: write, fix, and organize SQL faster and more accurately in [$CONSOLE][portal-ops-mode] for a $SERVICE_LONG.
+ - **psql**: easily run queries on your $SERVICE_LONGs or self-hosted TimescaleDB deployment from Terminal.
+
+
+
+
+
+## Write fast analytical queries on frequently access data using time buckets and continuous aggregates
+
+Aggregation is a way of combing data to get insights from it. Average, sum, and count are all
+example of simple aggregates. However, with large amounts of data aggregation slows things down, quickly.
+Continuous aggregates are a kind of hypertable that is refreshed automatically in
+the background as new data is added, or old data is modified. Changes to your dataset are tracked,
+and the hypertable behind the continuous aggregate is automatically updated in the background.
+
+You create continuous aggregates on uncompressed data in high-performance storage. They continue to work
+on [compressed frequently accessed data][test-drive-enable-compression]
+and [rarely accessed data in tiered storage][test-drive-tiered-storage]. You can even
+create [continuous aggregates on top of your continuous aggregates][hierarchical-caggs].
+
+You use time buckets to create a continuous aggregate. Time buckets aggregate data in hypertables by time
+interval. For example, a 5-minute, 1-hour, or 3-day bucket. The data grouped in a time bucket use a single
+timestamp. Continuous aggregates minimize the number of records that you need to look up to perform your
+query.
+
+This section show you how to run fast analytical queries using time buckets and continuous aggregates.
+
+
+
+1. **Create a continuous aggregate**
+
+ For a continuous aggregate, data grouped using a time bucket is stored in a
+ PostgreSQL `MATERIALIZED VIEW` in a hypertable. `timescaledb.continuous` ensures that this data
+ is always up to date.
+ In your SQL editor, use the following code to create a continuous aggregate on the real time data in
+ the `stocks_real_time` table:
+
+ ```sql
+ CREATE MATERIALIZED VIEW stock_candlestick_daily
+ WITH (timescaledb.continuous) AS
+ SELECT
+ time_bucket('1 day', "time") AS day,
+ symbol,
+ max(price) AS high,
+ first(price, time) AS open,
+ last(price, time) AS close,
+ min(price) AS low
+ FROM stocks_real_time srt
+ GROUP BY day, symbol;
+ ```
+
+ This continuous aggregate creates the [candlestick chart][charts] data you use to visualize
+ the price change of an asset.
+
+1. **Create a policy to refresh the view every hour**
+
+ ```sql
+ SELECT add_continuous_aggregate_policy('stock_candlestick_daily',
+ start_offset => INTERVAL '1 month',
+ end_offset => INTERVAL '1 day',
+ schedule_interval => INTERVAL '1 hour');
+ ```
+
+1. **Have a quick look at your data**
+
+ You query continuous aggregates exactly the same way as your other tables. To query the `stock_candlestick_daily`
+ continuous aggregate for all stocks:
+
+
+
+
+
+
+To see the change in terms of query time and data returned between a regular query and
+a continuous aggregate, run the query part of the continuous aggregate
+( `SELECT ...GROUP BY day, symbol;` ) and compare the results.
+
+## Reduce storage charges using compression
+
+Compressing your time-series data allows you to reduce your chunk size by more than 90%. This saves on
+storage costs, while your queries continue to operate at lightning speed.
+
+New data is added to your database in the form of uncompressed rows. When you enable
+compression, TimescaleDB uses a built-in job scheduler to compress the data in a hypertable
+chunk-by-chunk when it reaches a certain maturity. In a compressed chunk, multiple records are grouped into
+a single row. Best practice is to compress data that is no longer needed for highest performance queries, but
+is still access regularly. For example, last week's stock market data.
+
+
+
+1. **Enable compression**
+
+ In your SQL editor, use the following code to compress the data in a hypertable. In this example, the
+ hypertable is also a continuous aggregate:
+
+ ```sql
+ ALTER TABLE stock_candlestick_daily SET (
+ timescaledb.compress,
+ timescaledb.compress_segmentby = 'symbol'
+ );
+ ```
+
+1. **Set the time interval when data is compressed**
+
+ ```sql
+ SELECT add_compression_policy('stock_candlestick_daily', INTERVAL '7 days');
+ ```
+
+
+
+
+
+## Reduce storage charges for rarely accessed data using tiered storage
+
+In the previous sections, you used continuous aggregates to make fast analytical queries, and
+compression to reduce storage costs on frequently accessed data. To reduce storage costs even more,
+you create tiering policies to move rarely accessed data to the object store. The object store is
+low-cost bottomless data storage built on Amazon S3. However, no matter the tier, you can
+[query your data when you need][querying-tiered-data]. $CLOUD_LONG seamlessly accesses the correct storage
+tier and generates the response.
+
+Data tiering is available in the [scale and enterprise][pricing-plans] pricing plans for $CLOUD_LONG. Sign up for
+a [30 day free trial][sign-up] and try for free.
+
+To setup data tiering:
+
+
+
+1. **Enable data tiering**
+
+ 1. In [$CONSOLE][portal-ops-mode], select the service to modify.
+
+ You see the `Overview` section.
+
+ 1. Scroll down, then click `Enable tiered storage`.
+
+ 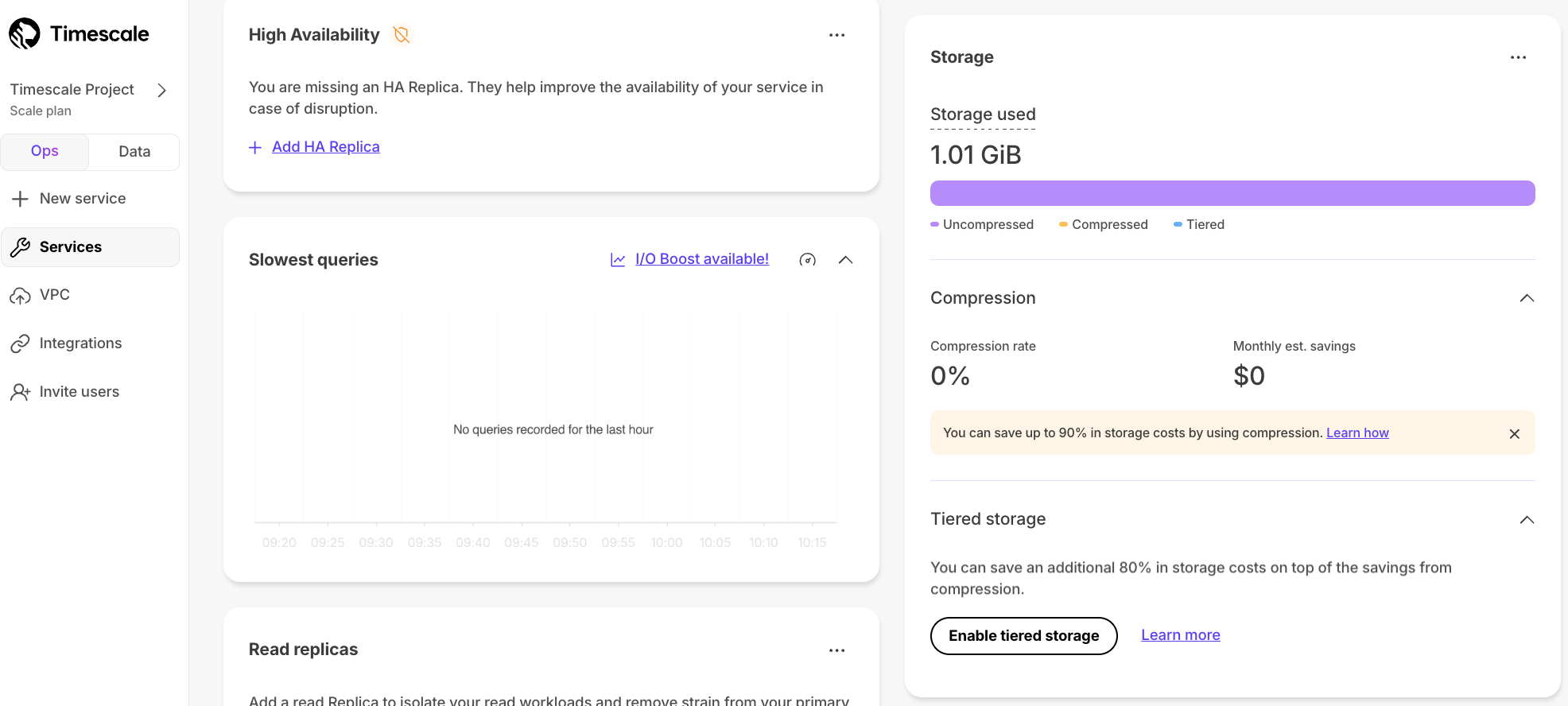
+
+ When tiered storage is enabled, you see the amount of data in the tiered object storage.
+
+1. **Set the time interval when data is tiered**
+
+ In $CONSOLE, click `SQL Editor`, then enable data tiering on a hypertable with the following query:
+ ```sql
+ SELECT add_tiering_policy('stock_candlestick_daily', INTERVAL '3 weeks');
+ ```
+
+1. **Qeury tiered data**
+
+ You enable reads from tiered data for each query, for a session or for all future
+ sessions. To run a single query on tiered data:
+
+ ```sql
+ set timescaledb.enable_tiered_reads = true; SELECT * FROM stocks_real_time srt LIMIT 10; set timescaledb.enable_tiered_reads = false;
+ ```
+ For more information, see [Querying tiered data][querying-tiered-data].
+
+
+
+## Reduce the risk of downtime and data loss with high availability
+
+By default, all $SERVICE_LONGs have rapid recovery enabled. However, if your app has very low tolerance
+for downtime, $CLOUD_LONG offers High Availability (HA) replicas. HA replicas are exact, up-to-date copies
+of your database hosted in multiple AWS availability zones (AZ) within the same region as your primary node.
+HA replicas automatically take over operations if the original primary data node becomes unavailable.
+The primary node streams its write-ahead log (WAL) to the replicas to minimize the chances of
+data loss during failover.
+
+High availability is available in the [scale and enterprise][pricing-plans] pricing plans for $CLOUD_LONG. Sign up for
+a [30 day free trial][sign-up] and try for free.
+
+
+
+For more information, see [High availability][high-availability].
+
+What next? See the [use case tutorials][tutorials], interact with the data in your $SERVICE_LONG using
+[your favorite programming language][connect-with-code], integrate your $SERVICE_LONG with a range of
+[third-party tools][integrations], plain old [Use Timescale][use-timescale], or dive into [the API][use-the-api].
+
+[tutorials]: /tutorials/:currentVersion:/
+[connect-with-code]: /quick-start/:currentVersion:/
+[integrations]: /use-timescale/:currentVersion:/integrations/
+[use-the-api]: /api/:currentVersion:/
+[use-timescale]: /use-timescale/:currentVersion:/
+
+[create-a-service]: /getting-started/:currentVersion:/services/
+[deploy-self-hosted]: /self-hosted/:currentVersion:/install/
+[connect-to-your-service]: /getting-started/:currentVersion:/run-queries-from-console/
+[portal-ops-mode]: https://console.cloud.timescale.com/dashboard/services
+[portal-data-mode]: https://console.cloud.timescale.com/dashboard/services?popsql
+[migrate-with-downtime]: /migrate/:currentVersion:/pg-dump-and-restore/
+[migrate-live]: /migrate/:currentVersion:/live-migration/
+[data-ingest]: /use-timescale/:currentVersion:/ingest-data/
+[hypertables-section]: /use-timescale/:currentVersion:/hypertables/
+[test-drive-enable-compression]: /getting-started/:currentVersion:/test-drive-timescale-features/#reduce-storage-charges-on-older-data-using-compression
+[test-drive-tiered-storage]: /getting-started/:currentVersion:/test-drive-timescale-features/#reduce-storage-charges-on-older-data-using-compression
+[data-tiering]: /use-timescale/:currentVersion:/data-tiering/
+[compression]: /use-timescale/:currentVersion:/compression/
+[hierarchical-caggs]: /use-timescale/:currentVersion:/continuous-aggregates/hierarchical-continuous-aggregates/
+[charts]: https://www.investopedia.com/terms/c/candlestick.asp
+[hierarchical-storage]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hierarchical_storage_management
+[querying-tiered-data]: /use-timescale/:currentVersion:/data-tiering/querying-tiered-data/
+[data-tiering]: /use-timescale/:currentVersion:/data-tiering/
+[pricing-plans]: /about/:currentVersion:/pricing-and-account-management
+[querying-tiered-data]: /use-timescale/:currentVersion:/data-tiering/querying-tiered-data/
+[high-availability]: /use-timescale/:currentVersion:/ha-replicas/high-availability/
+[sign-up]: https://console.cloud.timescale.com/signup
diff --git a/use-timescale/data-tiering/enabling-data-tiering.md b/use-timescale/data-tiering/enabling-data-tiering.md
index 9816326f78..d3b08d011d 100644
--- a/use-timescale/data-tiering/enabling-data-tiering.md
+++ b/use-timescale/data-tiering/enabling-data-tiering.md
@@ -34,14 +34,14 @@ You enable tiered storage from the `Overview` tab in Console.
When tiered storage is enabled, you see the amount of data in the tiered object storage.
-
-
- Data tiering is available in [Scale and Enterprise][pricing-plans] pricing plans only.
-
-
-
+
+
+Data tiering is available in [Scale and Enterprise][pricing-plans] pricing plans only.
+
+
+
## Automate tiering with policies
A tiering policy automatically moves any chunks that only contain data
diff --git a/use-timescale/ha-replicas/high-availability.md b/use-timescale/ha-replicas/high-availability.md
index 59194f43e3..48a0fc263d 100644
--- a/use-timescale/ha-replicas/high-availability.md
+++ b/use-timescale/ha-replicas/high-availability.md
@@ -9,6 +9,8 @@ cloud_ui:
- [services, :serviceId, operations, replication]
---
+import HASetup from 'versionContent/_partials/_high-availability-setup.mdx';
+
# Manage high availability
@@ -71,26 +73,12 @@ The `High` and `Highest` HA strategies are available with the [Scale and the Ent
To enable HA for a Timescale Cloud Service:
-
-
-1. In [Timescale Console][cloud-login], select the service to enable replication for.
-1. Click `Operations`, then select `High availability`.
-1. Choose your replication strategy, then click `Change configuration`.
-
+
+1. In `Change high availability configuration`, click `Change config`.
+
+
+
+[cloud-login]: https://console.cloud.timescale.com
diff --git a/_partials/_where-to-next.md b/_partials/_where-to-next.md
index 5d1124a297..e7501f1d62 100644
--- a/_partials/_where-to-next.md
+++ b/_partials/_where-to-next.md
@@ -1,7 +1,11 @@
-Now you have TimescaleDB running, have a look at the:
+What next? [Try the main features offered by Timescale][try-timescale-features], see the [use case tutorials][tutorials],
+interact with the data in your $SERVICE_LONG using [your favorite programming language][connect-with-code], integrate
+your $SERVICE_LONG with a range of [third-party tools][integrations], plain old [Use Timescale][use-timescale], or dive
+into [the API][use-the-api].
-* [Tutorials][tutorials]: walk through a variety of business scenarios using example datasets.
-* [Use Timescale][tsdb-docs]: browse the features available with TimescaleDB.
-
-[tsdb-docs]: /use-timescale/:currentVersion:/
[tutorials]: /tutorials/:currentVersion:/
+[connect-with-code]: /quick-start/:currentVersion:/
+[integrations]: /use-timescale/:currentVersion:/integrations/
+[use-the-api]: /api/:currentVersion:/
+[use-timescale]: /use-timescale/:currentVersion:/
+[try-timescale-features]: /getting-started/:currentVersion:/test-drive-timescale-features/
diff --git a/getting-started/index.md b/getting-started/index.md
index 8fe5d5f27a..1b1bc30aae 100644
--- a/getting-started/index.md
+++ b/getting-started/index.md
@@ -16,21 +16,28 @@ import WhereNext from "versionContent/_partials/_where-to-next.mdx";
This section shows you how to:
-1. [Create and connect to a Timescale service][services-create]
-1. [Run queries from Timescale Console][run-queries-from-console]
-1. [Ingest some real financial data into your database][ingest-data]
-1. [Construct some interesting queries][queries] Try out some live queries
-1. [Create and query a continuous aggregates][caggs]
+1. [Create and connect to a $SERVICE_LONG][services-create]: choose the capabilities that match your business and
+ engineering needs on $COMPANY's cloud-based PostgreSQL platform.
+1. [Run queries from $CONSOLE][run-queries-from-console]: securely interact your data in the $CONSOLE UI.
+1. [Try the main features in Timescale products][test-drive]: rapidly implement the features in $CLOUD_LONG that
+ enable you to ingest and query data faster while keeping prices low.
-Already know the basics? See the
-[more advanced tutorials][tutorials], or see how to
-[Use Timescale][use-timescale].
+What next? See the [use case tutorials][tutorials], interact with the data in your $SERVICE_LONG using
+[your favorite programming language][connect-with-code], integrate your $SERVICE_LONG with a range of
+[third-party tools][integrations], plain old [Use Timescale][use-timescale], or dive into [the API][use-the-api].
[tutorials]: /tutorials/:currentVersion:/
+[connect-with-code]: /quick-start/:currentVersion:/
+[integrations]: /use-timescale/:currentVersion:/integrations/
+[use-the-api]: /api/:currentVersion:/
[use-timescale]: /use-timescale/:currentVersion:/
+
+
[services-create]: /getting-started/:currentVersion:/services#create-your-timescale-account
[services-connect]: /getting-started/:currentVersion:/services/#connect-to-your-service
+[test-drive]: /getting-started/:currentVersion:/test-drive-timescale-features/
[run-queries-from-console]: /getting-started/:currentVersion:/run-queries-from-console/
[ingest-data]: /getting-started/:currentVersion:/time-series-data/
[queries]: /getting-started/:currentVersion:/queries/
[caggs]: /getting-started/:currentVersion:/aggregation/
+
diff --git a/getting-started/page-index/page-index.js b/getting-started/page-index/page-index.js
index ef51f973f8..17645679ae 100644
--- a/getting-started/page-index/page-index.js
+++ b/getting-started/page-index/page-index.js
@@ -15,29 +15,9 @@ module.exports = [
excerpt: "Run your queries securely from inside Timescale Console",
},
{
- title: "Tables and hypertables",
- href: "tables-hypertables",
- excerpt: "Create tables and hypertables for your data",
- },
- {
- title: "Time-series data",
- href: "time-series-data",
- excerpt: "Add time-series data to your database",
- },
- {
- title: "Queries",
- href: "queries",
- excerpt: "Query your data using full SQL",
- },
- {
- title: "Aggregation",
- href: "aggregation",
- excerpt: "Query aggregated data, and create a continuous aggregate",
- },
- {
- title: "Next steps",
- href: "next-steps",
- excerpt: "Get even more from your Timescale database",
+ title: "Try the main features in Timescale products",
+ href: "test-drive-timescale-features",
+ excerpt: "Improve database performance with Hypertables, time bucketing, continuous aggregates, compression, data tiering, and high availability",
},
],
},
diff --git a/getting-started/run-queries-from-console.md b/getting-started/run-queries-from-console.md
index e200244f32..f2a8a2f868 100644
--- a/getting-started/run-queries-from-console.md
+++ b/getting-started/run-queries-from-console.md
@@ -6,6 +6,8 @@ layout_components: [next_prev_large]
content_group: Getting started
---
+import WhereNext from "versionContent/_partials/_where-to-next.mdx";
+
# Run your queries from Timescale Console
As Timescale Cloud is based on PostgreSQL, you can use lots of [different tools][integrations] to
@@ -225,6 +227,7 @@ To use SQL editor with Timescale:
details.
+
[readreplica]: /use-timescale/:currentVersion:/ha-replicas/read-scaling/
[run-popsql]: /getting-started/:currentVersion:/run-queries-from-console/#data-mode
diff --git a/getting-started/services.md b/getting-started/services.md
index 105f80f60f..cc0c0f1af4 100644
--- a/getting-started/services.md
+++ b/getting-started/services.md
@@ -11,6 +11,7 @@ import Connect from "versionContent/_partials/_cloud-connect.mdx";
import CreateAHypertable from "versionContent/_partials/_create-hypertable.mdx";
import ServiceOverview from "versionContent/_partials/_service-overview.mdx";
import CloudIntro from "versionContent/_partials/_cloud-intro.mdx";
+import WhereNext from "versionContent/_partials/_where-to-next.mdx";
# Create your first $SERVICE_LONG
@@ -59,11 +60,10 @@ A Timescale service comes with access control to its data. To be able to run que
-## Create a hypertable
+And that is it, you are up and running. Enjoy developing with $COMPANY.
-
+
-And that is it, you are up and running. Enjoy developing with $COMPANY.
[tsc-portal]: https://console.cloud.timescale.com/
[services-how-to]: /use-timescale/:currentVersion:/services/
diff --git a/getting-started/test-drive-timescale-features.md b/getting-started/test-drive-timescale-features.md
new file mode 100644
index 0000000000..ad5f015318
--- /dev/null
+++ b/getting-started/test-drive-timescale-features.md
@@ -0,0 +1,344 @@
+---
+title: Try the main features in Timescale products
+excerpt: Improve database performance with hypertables, time bucketing, compression and continuous aggregates.
+products: [cloud]
+content_group: Getting started
+---
+
+import HASetup from 'versionContent/_partials/_high-availability-setup.mdx';
+
+# Try the main features in Timescale products
+
+$CLOUD_LONG scales PostgreSQL to ingest and query vast amounts of live data. $CLOUD_LONG
+provides a range of features and optimizations that supercharge your queries while keeping the
+costs down. For example:
+* The row-columnar engine makes queries up to 350x faster, ingests 44% faster, and reduces storage by 95%.
+* Tiered storage seamlessly moves your data from high performance storage for frequently access data to low cost bottomless storage for rarely accessed data.
+
+You use the same optimization methods for data in all storage tiers:
+
+
+
+This page gives shows you how to rapidly implement the features in $CLOUD_LONG that enable you to
+ingest and query data faster while keeping prices low.
+
+## Prerequisites
+
+To run the examples in this page, you need either:
+- A [$SERVICE_LONG][create-a-service] with time-series and ai and vector capabilities enabled.
+- A [self-hosted PostgreSQL deployment][deploy-self-hosted] with the TimescaleDB, pgvector, pgvectorscale and
+ pgai extensions enabled in your database.
+
+## Optimize time-series data in hypertables
+
+Hypertables are PostgreSQL tables that help you improve insert and query
+performance by automatically partition your data by time. Each hypertable is made
+up of child tables called chunks. Each chunk is assigned a range of time, and only
+contains data from that range. You can also tune hypertables to increase performance
+even more.
+
+Hypertables exist alongside regular PostgreSQL tables.
+You use regular PostgreSQL tables for relational data, and interact with hypertables
+and regular PostgreSQL tables in the same way.
+
+This section shows you how to create regular tables and hypertables, and import
+relational and time-series data from external files.
+
+
+
+1. **Import some time-series data into your hypertable**
+
+ 1. Unzip [real_time_stock_data.zip](https://assets.timescale.com/docs/downloads/get-started/real_time_stock_data.zip) to a ``.
+
+ This test dataset contains second-by-second stock-trade data for the top 100 most-traded symbols
+ and a regular table of company symbols and company names.
+
+ To import up to 100GB of data directly from your current PostgreSQL based database,
+ [migrate with downtime][migrate-with-downtime] using native PostgreSQL tooling. To seamlessly import 100GB-10TB+
+ of data, use the [live migration][migrate-live] tooling supplied by $COMPANY. To add data from non-PostgreSQL
+ data sources, see [Import and ingest data][data-ingest].
+
+ 1. Upload data from the CSV files to your $SERVICE_SHORT:
+
+
+
+
+
+ The $CONSOLE data upload creates the tables for you from the data you are uploading:
+ 1. In [$CONSOLE][portal-ops-mode], select the service to add data to, then click **Actions** > **Upload CSV**.
+ 1. Drag `/tutorial_sample_company.csv`.
+ 1. Change `New table name` to `company`, then click `Upload CSV`.
+ 1. Use the same process to upload `/tutorial_sample_tick.csv` to the `stocks_real_time` table.
+ 1. Convert the `stocks_real_time relational` relational table to a hypertable.
+
+ In $CONSOLE. click `SQL editor`, then run the following query:
+
+ ```sql
+ SELECT create_hypertable('stocks_real_time', by_range('time'), migrate_data => TRUE);
+ ```
+
+ To more fully understand how hypertables work, and how to optimize them for performance by
+ tuning chunk intervals and enabling chunk skipping, see [the hypertables documentation][hypertables-section].
+
+
+
+
+
+ 1. In Terminal, navigate to `` and connect to your $SERVICE_SHORT.
+ ```bash
+ psql -d "postgres://:@:/"
+ ```
+ The connection information for a $SERVICE_SHORT is available in the file you downloaded when you created it.
+
+ 2. Create tables for the data to import
+
+ - For the time-series data:
+ 1. In your sql client, create a normal PostgreSQL table:
+
+ ```sql
+ CREATE TABLE stocks_real_time (
+ time TIMESTAMPTZ NOT NULL,
+ symbol TEXT NOT NULL,
+ price DOUBLE PRECISION NULL,
+ day_volume INT NULL
+ );
+ ```
+ 1. Convert `stocks_real_time` to a hypertable:
+ ```sql
+ SELECT create_hypertable('stocks_real_time', by_range('time'));
+ ```
+ To more fully understand how hypertables work, and how to optimize them for performance by
+ tuning chunk intervals and enabling chunk skipping, see [the hypertables documentation][hypertables-section].
+
+ - For the relational data:
+
+ In your sql client, create a normal PostgreSQL table:
+ ```sql
+ CREATE TABLE company (
+ symbol TEXT NOT NULL,
+ name TEXT NOT NULL
+ );
+ ```
+
+ 3. Upload the dataset to your $SERVICE_SHORT
+ ```sql
+ \COPY stocks_real_time from './tutorial_sample_tick.csv' DELIMITER ',' CSV HEADER;
+ \COPY company from './tutorial_sample_company.csv' DELIMITER ',' CSV HEADER;
+ ```
+
+
+
+
+
+1. **Have a quick look at your data**
+
+ You query hypertables in exactly the same way as you would a relational PostgreSQL table.
+ Use one of the following SQL editors to run a query and see the data you uploaded:
+ - **Data mode**: write queries, visualize data, and share your results in [$CONSOLE][portal-data-mode] for all your $SERVICE_LONGs.
+ - **SQL editor**: write, fix, and organize SQL faster and more accurately in [$CONSOLE][portal-ops-mode] for a $SERVICE_LONG.
+ - **psql**: easily run queries on your $SERVICE_LONGs or self-hosted TimescaleDB deployment from Terminal.
+
+
+
+
+
+## Write fast analytical queries on frequently access data using time buckets and continuous aggregates
+
+Aggregation is a way of combing data to get insights from it. Average, sum, and count are all
+example of simple aggregates. However, with large amounts of data aggregation slows things down, quickly.
+Continuous aggregates are a kind of hypertable that is refreshed automatically in
+the background as new data is added, or old data is modified. Changes to your dataset are tracked,
+and the hypertable behind the continuous aggregate is automatically updated in the background.
+
+You create continuous aggregates on uncompressed data in high-performance storage. They continue to work
+on [compressed frequently accessed data][test-drive-enable-compression]
+and [rarely accessed data in tiered storage][test-drive-tiered-storage]. You can even
+create [continuous aggregates on top of your continuous aggregates][hierarchical-caggs].
+
+You use time buckets to create a continuous aggregate. Time buckets aggregate data in hypertables by time
+interval. For example, a 5-minute, 1-hour, or 3-day bucket. The data grouped in a time bucket use a single
+timestamp. Continuous aggregates minimize the number of records that you need to look up to perform your
+query.
+
+This section show you how to run fast analytical queries using time buckets and continuous aggregates.
+
+
+
+1. **Create a continuous aggregate**
+
+ For a continuous aggregate, data grouped using a time bucket is stored in a
+ PostgreSQL `MATERIALIZED VIEW` in a hypertable. `timescaledb.continuous` ensures that this data
+ is always up to date.
+ In your SQL editor, use the following code to create a continuous aggregate on the real time data in
+ the `stocks_real_time` table:
+
+ ```sql
+ CREATE MATERIALIZED VIEW stock_candlestick_daily
+ WITH (timescaledb.continuous) AS
+ SELECT
+ time_bucket('1 day', "time") AS day,
+ symbol,
+ max(price) AS high,
+ first(price, time) AS open,
+ last(price, time) AS close,
+ min(price) AS low
+ FROM stocks_real_time srt
+ GROUP BY day, symbol;
+ ```
+
+ This continuous aggregate creates the [candlestick chart][charts] data you use to visualize
+ the price change of an asset.
+
+1. **Create a policy to refresh the view every hour**
+
+ ```sql
+ SELECT add_continuous_aggregate_policy('stock_candlestick_daily',
+ start_offset => INTERVAL '1 month',
+ end_offset => INTERVAL '1 day',
+ schedule_interval => INTERVAL '1 hour');
+ ```
+
+1. **Have a quick look at your data**
+
+ You query continuous aggregates exactly the same way as your other tables. To query the `stock_candlestick_daily`
+ continuous aggregate for all stocks:
+
+
+
+
+
+
+To see the change in terms of query time and data returned between a regular query and
+a continuous aggregate, run the query part of the continuous aggregate
+( `SELECT ...GROUP BY day, symbol;` ) and compare the results.
+
+## Reduce storage charges using compression
+
+Compressing your time-series data allows you to reduce your chunk size by more than 90%. This saves on
+storage costs, while your queries continue to operate at lightning speed.
+
+New data is added to your database in the form of uncompressed rows. When you enable
+compression, TimescaleDB uses a built-in job scheduler to compress the data in a hypertable
+chunk-by-chunk when it reaches a certain maturity. In a compressed chunk, multiple records are grouped into
+a single row. Best practice is to compress data that is no longer needed for highest performance queries, but
+is still access regularly. For example, last week's stock market data.
+
+
+
+1. **Enable compression**
+
+ In your SQL editor, use the following code to compress the data in a hypertable. In this example, the
+ hypertable is also a continuous aggregate:
+
+ ```sql
+ ALTER TABLE stock_candlestick_daily SET (
+ timescaledb.compress,
+ timescaledb.compress_segmentby = 'symbol'
+ );
+ ```
+
+1. **Set the time interval when data is compressed**
+
+ ```sql
+ SELECT add_compression_policy('stock_candlestick_daily', INTERVAL '7 days');
+ ```
+
+
+
+
+
+## Reduce storage charges for rarely accessed data using tiered storage
+
+In the previous sections, you used continuous aggregates to make fast analytical queries, and
+compression to reduce storage costs on frequently accessed data. To reduce storage costs even more,
+you create tiering policies to move rarely accessed data to the object store. The object store is
+low-cost bottomless data storage built on Amazon S3. However, no matter the tier, you can
+[query your data when you need][querying-tiered-data]. $CLOUD_LONG seamlessly accesses the correct storage
+tier and generates the response.
+
+Data tiering is available in the [scale and enterprise][pricing-plans] pricing plans for $CLOUD_LONG. Sign up for
+a [30 day free trial][sign-up] and try for free.
+
+To setup data tiering:
+
+
+
+1. **Enable data tiering**
+
+ 1. In [$CONSOLE][portal-ops-mode], select the service to modify.
+
+ You see the `Overview` section.
+
+ 1. Scroll down, then click `Enable tiered storage`.
+
+ 
+
+ When tiered storage is enabled, you see the amount of data in the tiered object storage.
+
+1. **Set the time interval when data is tiered**
+
+ In $CONSOLE, click `SQL Editor`, then enable data tiering on a hypertable with the following query:
+ ```sql
+ SELECT add_tiering_policy('stock_candlestick_daily', INTERVAL '3 weeks');
+ ```
+
+1. **Qeury tiered data**
+
+ You enable reads from tiered data for each query, for a session or for all future
+ sessions. To run a single query on tiered data:
+
+ ```sql
+ set timescaledb.enable_tiered_reads = true; SELECT * FROM stocks_real_time srt LIMIT 10; set timescaledb.enable_tiered_reads = false;
+ ```
+ For more information, see [Querying tiered data][querying-tiered-data].
+
+
+
+## Reduce the risk of downtime and data loss with high availability
+
+By default, all $SERVICE_LONGs have rapid recovery enabled. However, if your app has very low tolerance
+for downtime, $CLOUD_LONG offers High Availability (HA) replicas. HA replicas are exact, up-to-date copies
+of your database hosted in multiple AWS availability zones (AZ) within the same region as your primary node.
+HA replicas automatically take over operations if the original primary data node becomes unavailable.
+The primary node streams its write-ahead log (WAL) to the replicas to minimize the chances of
+data loss during failover.
+
+High availability is available in the [scale and enterprise][pricing-plans] pricing plans for $CLOUD_LONG. Sign up for
+a [30 day free trial][sign-up] and try for free.
+
+
+
+For more information, see [High availability][high-availability].
+
+What next? See the [use case tutorials][tutorials], interact with the data in your $SERVICE_LONG using
+[your favorite programming language][connect-with-code], integrate your $SERVICE_LONG with a range of
+[third-party tools][integrations], plain old [Use Timescale][use-timescale], or dive into [the API][use-the-api].
+
+[tutorials]: /tutorials/:currentVersion:/
+[connect-with-code]: /quick-start/:currentVersion:/
+[integrations]: /use-timescale/:currentVersion:/integrations/
+[use-the-api]: /api/:currentVersion:/
+[use-timescale]: /use-timescale/:currentVersion:/
+
+[create-a-service]: /getting-started/:currentVersion:/services/
+[deploy-self-hosted]: /self-hosted/:currentVersion:/install/
+[connect-to-your-service]: /getting-started/:currentVersion:/run-queries-from-console/
+[portal-ops-mode]: https://console.cloud.timescale.com/dashboard/services
+[portal-data-mode]: https://console.cloud.timescale.com/dashboard/services?popsql
+[migrate-with-downtime]: /migrate/:currentVersion:/pg-dump-and-restore/
+[migrate-live]: /migrate/:currentVersion:/live-migration/
+[data-ingest]: /use-timescale/:currentVersion:/ingest-data/
+[hypertables-section]: /use-timescale/:currentVersion:/hypertables/
+[test-drive-enable-compression]: /getting-started/:currentVersion:/test-drive-timescale-features/#reduce-storage-charges-on-older-data-using-compression
+[test-drive-tiered-storage]: /getting-started/:currentVersion:/test-drive-timescale-features/#reduce-storage-charges-on-older-data-using-compression
+[data-tiering]: /use-timescale/:currentVersion:/data-tiering/
+[compression]: /use-timescale/:currentVersion:/compression/
+[hierarchical-caggs]: /use-timescale/:currentVersion:/continuous-aggregates/hierarchical-continuous-aggregates/
+[charts]: https://www.investopedia.com/terms/c/candlestick.asp
+[hierarchical-storage]: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hierarchical_storage_management
+[querying-tiered-data]: /use-timescale/:currentVersion:/data-tiering/querying-tiered-data/
+[data-tiering]: /use-timescale/:currentVersion:/data-tiering/
+[pricing-plans]: /about/:currentVersion:/pricing-and-account-management
+[querying-tiered-data]: /use-timescale/:currentVersion:/data-tiering/querying-tiered-data/
+[high-availability]: /use-timescale/:currentVersion:/ha-replicas/high-availability/
+[sign-up]: https://console.cloud.timescale.com/signup
diff --git a/use-timescale/data-tiering/enabling-data-tiering.md b/use-timescale/data-tiering/enabling-data-tiering.md
index 9816326f78..d3b08d011d 100644
--- a/use-timescale/data-tiering/enabling-data-tiering.md
+++ b/use-timescale/data-tiering/enabling-data-tiering.md
@@ -34,14 +34,14 @@ You enable tiered storage from the `Overview` tab in Console.
When tiered storage is enabled, you see the amount of data in the tiered object storage.
-
-
- Data tiering is available in [Scale and Enterprise][pricing-plans] pricing plans only.
-
-
-
+
+
+Data tiering is available in [Scale and Enterprise][pricing-plans] pricing plans only.
+
+
+
## Automate tiering with policies
A tiering policy automatically moves any chunks that only contain data
diff --git a/use-timescale/ha-replicas/high-availability.md b/use-timescale/ha-replicas/high-availability.md
index 59194f43e3..48a0fc263d 100644
--- a/use-timescale/ha-replicas/high-availability.md
+++ b/use-timescale/ha-replicas/high-availability.md
@@ -9,6 +9,8 @@ cloud_ui:
- [services, :serviceId, operations, replication]
---
+import HASetup from 'versionContent/_partials/_high-availability-setup.mdx';
+
# Manage high availability
@@ -71,26 +73,12 @@ The `High` and `Highest` HA strategies are available with the [Scale and the Ent
To enable HA for a Timescale Cloud Service:
-
-
-1. In [Timescale Console][cloud-login], select the service to enable replication for.
-1. Click `Operations`, then select `High availability`.
-1. Choose your replication strategy, then click `Change configuration`.
-  -
-1. In `Change high availability configuration`, click `Change config`.
+
To change your HA replica strategy, click `Change configuration`, choose a strategy and click `Change configuration`.
To download the connection information for the HA replica, either click the link next to the replica
`Active configuration`, or find the information in the `Overview` tab for this service.
-
-
-
## Test failover for your HA replicas
To test the failover mechanism, you can trigger a switchover. A switchover is a
-
-1. In `Change high availability configuration`, click `Change config`.
+
To change your HA replica strategy, click `Change configuration`, choose a strategy and click `Change configuration`.
To download the connection information for the HA replica, either click the link next to the replica
`Active configuration`, or find the information in the `Overview` tab for this service.
-
-
-
## Test failover for your HA replicas
To test the failover mechanism, you can trigger a switchover. A switchover is a
 +
+1. In `Change high availability configuration`, click `Change config`.
+
+
+
+1. In `Change high availability configuration`, click `Change config`.
+
+ +
+1. In `Change high availability configuration`, click `Change config`.
+
+
+
+1. In `Change high availability configuration`, click `Change config`.
+
+ -
-1. In `Change high availability configuration`, click `Change config`.
+
-
-1. In `Change high availability configuration`, click `Change config`.
+