#RemoteDebug Library for ESP8266
Works with the ESP8266 Arduino platform v2.0.0 or higher. Refer to https://github.com/esp8266/Arduino
By default the Arduino only has as debug possibility via the Serial port. This has a few disadvantages:
- requires a physical cable to the Arduino device (if the device is far away or in a remote location this is not easy)
- debugging multiple Arduinos at the same time requires many serial ports and a lot of cables
With the ESP8266 (NodeMCU) we now have network connectivity which can be used for streaming debugging information in real-time.
Telnet is a standard way of remotely connecting to a server and is supported on all operating systems (Windows, Mac, Linux...). A typical telnet client for Windows is Putty for example.
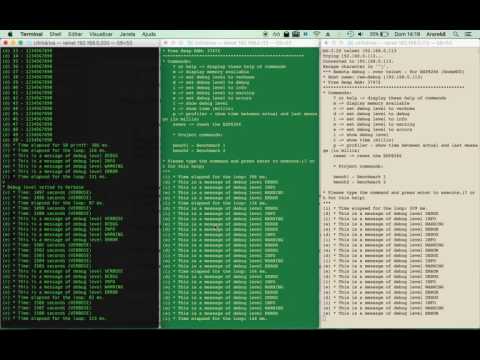
RemoteDebug sets-up a telnet server which is listening to any telnet client that wants to connect. After connection, logging is streamed to the telenet client.
RemoteDebug is very simple to use, after a few lines of initialization code, you can use the well-known "print" commands to stream your logging to the remote client.
RemoteDebug supports the filtering of logging based on debug levels:
- Verbose
- Debug
- Info
- Warnings
- Errors
These levels are in the order of most-logging -> least-logging.
The telnet client can set the debug level by typing a few simple commands.
RemoteDebug includes a simple profiler. It can be enabled by the connected telnet client or the Arduino code itself.
When enabled, it shows the time between 2 debug statements, using different colors depending on the elapsed time.
A typical example would be to insert logging just before and after a function after which you can see how much the is spend in the function.
RemoteDebug is designed to give minimal overhead if there is not telnet client connected.
RemoteDebug supports custom commands that can be entered in the telnet client. These trigger the execution of a custom function in the Arduino code. For example this can be used to send back a status on request of the telnet client.
Also please see my another library: https://github.com/JoaoLopesF/ArduinoUtil
##Warning
In beta versions, the isActive method was misspelled, Please when upgrading from a beta to the current one, please review your code.
From:
if (Debug.ative(Debug.<level>)) ....
To:
if (Debug.isActive(Debug.<level>)) ....
##DISCLAIMER:
The current version of RemoteDebug does not yet include any authentication and is intended only for development.
Future extension could include a secure way for authentication and further testing to support production environments.
- Http page to begin/stop the telnet server
- Authentication
- Support for production environment
![Imgur] (http://i.imgur.com/QiccbmK.png)
###includes
#include <ESP8266WiFi.h> //ESP8266 Core WiFi Library (you most likely already have this in your sketch)#include "RemoteDebug.h" // Remote debug over telnet - not recommended for production, only for development ###setup
- In the setup function after WiFi initialization
// Initialize the telnet server of RemoteDebug
Debug.begin("Telnet_HostName"); // Initiaze the telnet server
// OR
Debug.begin(HOST_NAME); // Initiaze the telnet server - HOST_NAME is the used in MDNS.begin
Debug.setResetCmdEnabled(true); // Enable the reset command
//Debug.showTime(true); // To show time
// Debug.showProfiler(true); // To show profiler - time between messages of Debug
- In the tail of loop function
// Remote debug over telnet
Debug.handle();
- In any place of you code:
if (Debug.isActive(Debug.<level>)) {
Debug.printf("bla bla bla: %d %s\n", number, str); // OR
Debug.printf("bla bla bla: %d %s\n", number, str.c_str()); // Note: if type is String need c_str() // OR
Debug.println("bla bla bla 2 ln");
// Note: to show floats with printf,
// you can use my ArduinoUtil library -> https://github.com/JoaoLopesF/ArduinoUtil
Debug.printf("float: %f\n", value); // Not works :-(
Debug.printf("float: %s\n", Util.formatFloat(value, 0, 5).c_str());
}- An example of use debug levels: (supposing the data is a lot of characteres)
if (Debug.isActive(Debug.VERBOSE)) { // Debug message long
Debug.printf("routine: data received: %s\n", data.c_str()); // Note: if type is String need c_str()
} else if (Debug.isActive(Debug.DEBUG)) { // Debug message short
Debug.printf("routine: data received: %s ...\n", data.substring(0, 20).c_str()); // %.20s not working :-|
}- An example of use debug with serial enabled Useful to see messages if setup or in cause the ESP8266 is rebooting (telnet connection stop before received all messages) Only for this purposes I suggest it
// Setup after Debug.begin
Debug.setSerialEnabled(true);
// All messages too send to serial too, and can be see in serial monitor
-
For reduce overheads RemoteDebug is disconnect the telnet client if it not active.
-
Please pless enter or any key if you need keep the connection
-
The default is 5 minutes (You can change it in RemoteDebug.h)
-
You can use mDNS to register each node with different name, it helps to connect without know the IP.
-
Please not forget to use if clause with Debug.isActive ---> This is very important to reduce overheads and work of debug levels
-
Please see the samples, basic or advanced, to learn how to use
-
In advanced sample, I used WifiManager library, ArduinoOTA and mDNS, please see it.
Adjustments and improvements from Beta versions. News features:
- Filter
- Colors
- Support to Windows telnet client
- First Beta
- Sometimes (rarely) the connection over telnet becomes very slow. Especially right after uploading firmware. Reset command in telnet connection or turn off/on can be resolve it. But I need find why it occurs
First thanks a lot for Igrr for bring to us the Arduino ESP8266.
Resources:
- Example of TelnetServer code in http://www.rudiswiki.de/wiki9/WiFiTelnetServer