Vulnerability scanner for Linux/FreeBSD, agentless, written in golang.
We have a slack team. Join slack team
Twitter: @vuls_en
- Vuls: VULnerability Scanner
- TOC
- Abstract
- Main Features
- What Vuls Doesn't Do
- Setup Vuls
- Tutorial
- Tutorial: Local Scan Mode
- Tutorial: Remote Scan Mode
- Setup Vuls in a Docker Container
- Architecture
- Use Cases
- Support OS
- Usage: Automatic Server Discovery
- Configuration
- Usage: Configtest
- Usage: Scan
- Usage: Report
- How to read a report
- Example: Send scan results to Slack
- Example: Put results in S3 bucket
- Example: Put results in Azure Blob storage
- Example: IgnoreCves
- Example: Add optional key-value pairs to JSON
- Example: Use MySQL as a DB storage back-end
- Example: Use PostgreSQL as a DB storage back-end
- Example: Use Redis as a DB storage back-end
- Usage: Scan vulnerabilites of non-OS packages
- Usage: Integrate with OWASP Dependency Check to Automatic update when the libraries are updated (Experimental)
- Usage: TUI
- Display the previous scan results using peco
- Usage: go-cve-dictionary on different server
- Usage: Update NVD Data
- Usage: goval-dictionary on different server
- Usage: Update OVAL Data
- How to Update to the Latest Version
- Misc
- Related Projects
- Data Source
- Authors
- Contribute
- Change Log
- Stargazers over time
- License
Created by gh-md-toc
For a system administrator, having to perform security vulnerability analysis and software update on a daily basis can be a burden. To avoid downtime in production environment, it is common for system administrator to choose not to use the automatic update option provided by package manager and to perform update manually. This leads to the following problems.
- System administrator will have to constantly watch out for any new vulnerabilities in NVD(National Vulnerability Database) or similar databases.
- It might be impossible for the system administrator to monitor all the software if there are a large number of software installed in server.
- It is expensive to perform analysis to determine the servers affected by new vulnerabilities. The possibility of overlooking a server or two during analysis is there.
Vuls is a tool created to solve the problems listed above. It has the following characteristics.
- Informs users of the vulnerabilities that are related to the system.
- Informs users of the servers that are affected.
- Vulnerability detection is done automatically to prevent any oversight.
- Report is generated on regular basis using CRON or other methods. to manage vulnerability.
- Scan for any vulnerabilities in Linux/FreeBSD Server
- Supports Alpine, Ubuntu, Debian, CentOS, Amazon Linux, RHEL, Oracle Linux, SUSE Enterprise Linux and Raspbian, FreeBSD
- Cloud, on-premise, Docker
- High quality scan
- Vuls uses Multiple vulnerability databases
- OVAL
- RHSA/ALAS/ELSA/FreeBSD-SA
- Changelog
- Vuls uses Multiple vulnerability databases
- Fast scan and Deep scan
- Fast Scan
- Scan without root privilege
- Scan with No internet access. (RedHat, CentOS, OracleLinux, Ubuntu, Debian)
- Almost no load on the scan target server
- Deep Scan
- Scan with root privilege
- Parses the Changelog
Changelog has a history of version changes. When a security issue is fixed, the relevant CVE ID is listed. By parsing the changelog and analysing the updates between the installed version of software on the server and the newest version of that software it's possible to create a list of all vulnerabilities that need to be fixed. - Sometimes load on the scan target server
- Fast Scan
- Remote scan and Local scan
- Remote Scan
- User is required to only setup one machine that is connected to other target servers via SSH
- Local Scan
- If you don't want the central Vuls server to connect to each server by SSH, you can use Vuls in the Local Scan mode.
- Remote Scan
- Dynamic Analysis
- It is possible to acquire the state of the server by connecting via SSH and executing the command
- Vuls warns when the scan target server was updated the kernel etc. but not restarting it.
- It is possible to acquire the state of the server by connecting via SSH and executing the command
- Scan middleware that are not included in OS package management
- Scan middleware, programming language libraries and framework for vulnerability
- Support software registered in CPE
- Nondestructive testing
- Pre-authorization is NOT necessary before scanning on AWS
- Vuls works well with Continuous Integration since tests can be run every day. This allows you to find vulnerabilities very quickly.
- Auto generation of configuration file template
- Auto detection of servers set using CIDR, generate configuration file template
- Email and Slack notification is possible (supports Japanese language)
- Scan result is viewable on accessory software, TUI Viewer on terminal or Web UI (VulsRepo).
- Vuls doesn't update the vulnerable packages.
There are 2 ways to setup Vuls.
-
Docker container
Dockernized-Vuls with vulsrepo UI in it.
You can run install and run Vuls on your machine with only a few commands.
see https://github.com/future-architect/vuls/tree/master/setup/docker -
Manually
Tutorial shows how to setup vuls manually.
To give you an idea of how easy Vuls is to use. This tutorial consists of three steps.
- Tutorial: Local Scan Mode
- Launch CentOS on AWS
- Deploy Vuls
- Scan localhost, Reporting
- Tutorial: Remote Scan Mode
- Launch Ubuntu Linux on AWS
- Scan this Ubuntu from the Vuls you set up earlier
This tutorial will let you scan the vulnerabilities on the localhost with Vuls.
This can be done in the following steps.
- Launch CentOS
- Install requirements
- Deploy go-cve-dictionary
- Deploy goval-dictionary
- Deploy Vuls
- Configuration
- Check config.toml and settings on the server before scanning
- Scan
- Reporting
- TUI(Terminal-Based User Interface)
- Web UI (VulsRepo)
-
We are using the old AMI for this example
-
Add the following to the cloud-init, to avoid auto-update at the first launch.
#cloud-config repo_upgrade: none
Vuls requires the following packages.
- SQLite3, MySQL, PostgreSQL, Redis
- git
- gcc
- GNU Make
- go v1.8.3 or later (The latest version is recommended)
$ ssh [email protected] -i ~/.ssh/private.pem
$ sudo yum -y install sqlite git gcc make wget
$ wget https://storage.googleapis.com/golang/go1.8.3.linux-amd64.tar.gz
$ sudo tar -C /usr/local -xzf go1.8.3.linux-amd64.tar.gz
$ mkdir $HOME/goAdd these lines into /etc/profile.d/goenv.sh
export GOROOT=/usr/local/go
export GOPATH=$HOME/go
export PATH=$PATH:$GOROOT/bin:$GOPATH/binSet the OS environment variable to current shell
$ source /etc/profile.d/goenv.sh$ sudo mkdir /var/log/vuls
$ sudo chown centos /var/log/vuls
$ sudo chmod 700 /var/log/vuls
$
$ mkdir -p $GOPATH/src/github.com/kotakanbe
$ cd $GOPATH/src/github.com/kotakanbe
$ git clone https://github.com/kotakanbe/go-cve-dictionary.git
$ cd go-cve-dictionary
$ make installThe binary was built under $GOPATH/bin
If the installation process stops halfway, try increasing the instance type of EC2. An out of memory error may have occurred.
Fetch vulnerability data from NVD.
It takes about 10 minutes (on AWS).
$ cd $HOME
$ for i in `seq 2002 $(date +"%Y")`; do go-cve-dictionary fetchnvd -years $i; done
... snip ...
$ ls -alh cve.sqlite3
-rw-r--r--. 1 centos centos 51M Aug 6 08:10 cve.sqlite3
-rw-r--r--. 1 centos centos 32K Aug 6 08:10 cve.sqlite3-shm
-rw-r--r--. 1 centos centos 5.1M Aug 6 08:10 cve.sqlite3-wal$ mkdir -p $GOPATH/src/github.com/kotakanbe
$ cd $GOPATH/src/github.com/kotakanbe
$ git clone https://github.com/kotakanbe/goval-dictionary.git
$ cd goval-dictionary
$ make installThe binary was built under $GOPATH/bin
If the installation process stops halfway, try increasing the instance type of EC2. An out of memory error may have occurred.
Then fetch OVAL data of RedHat since the server to be scanned is CentOS. README
$ goval-dictionary fetch-redhat 7If you want to scan other than CentOS 7, fetch OVAL data according to the OS type and version of scan target server in advance.
Launch a new terminal and SSH to the ec2 instance.
$ mkdir -p $GOPATH/src/github.com/future-architect
$ cd $GOPATH/src/github.com/future-architect
$ git clone https://github.com/future-architect/vuls.git
$ cd vuls
$ make install
If you have previously installed vuls and want to update, please do the following
$ rm -rf $GOPATH/pkg/linux_amd64/github.com/future-architect/vuls/
$ rm -rf $GOPATH/src/github.com/future-architect/vuls/
$ cd $GOPATH/src/github.com/future-architect
$ git clone https://github.com/future-architect/vuls.git
$ cd vuls
$ make install
The binary was built under $GOPATH/bin
If the installation process stops halfway, try increasing the instance type of EC2. An out of memory error may have occurred.
Create a config file(TOML format).
$ cd $HOME
$ cat config.toml
[servers]
[servers.localhost]
host = "localhost"
port = "local"
$ vuls configtest
$ vuls scan
... snip ...
One Line Summary
================
localhost centos7.3.1611 31 updatable packages
View one-line summary
$ vuls report -format-one-line-text -cvedb-path=$PWD/cve.sqlite3 -ovaldb-path=$PWD/oval.sqlite3
One Line Summary
================
localhost Total: 109 (High:35 Medium:55 Low:16 ?:3) 31 updatable packages
View short summary
$ vuls report -format-short-text
localhost (centos7.3.1611)
==========================
Total: 109 (High:35 Medium:55 Low:16 ?:3) 31 updatable packages
CVE-2015-2806 10.0 HIGH (nvd)
Stack-based buffer overflow in asn1_der_decoding in libtasn1 before 4.4 allows
remote attackers to have unspecified impact via unknown vectors.
---
https://nvd.nist.gov/vuln/detail/CVE-2015-2806
https://access.redhat.com/security/cve/CVE-2015-2806 (RHEL-CVE)
10.0/AV:N/AC:L/Au:N/C:C/I:C/A:C (nvd)
2.6/AV:N/AC:H/Au:N/C:N/I:N/A:P (redhat)
https://nvd.nist.gov/vuln-metrics/cvss/v2-calculator?name=CVE-2015-2806
3.3/CVSS:3.0/AV:L/AC:L/PR:N/UI:R/S:U/C:N/I:N/A:L (redhat)
https://nvd.nist.gov/vuln-metrics/cvss/v3-calculator?name=CVE-2015-2806
Confidence: 100 / OvalMatch
... snip ...
View full report.
$ vuls report -format-full-text | less
localhost (centos7.3.1611)
==========================
Total: 109 (High:35 Medium:55 Low:16 ?:3) 31 updatable packages
CVE-2015-2806
----------------
Max Score 10.0 HIGH (nvd)
nvd 10.0/AV:N/AC:L/Au:N/C:C/I:C/A:C
redhat 2.6/AV:N/AC:H/Au:N/C:N/I:N/A:P
redhat 3.3/CVSS:3.0/AV:L/AC:L/PR:N/UI:R/S:U/C:N/I:N/A:L
CVSSv2 Calc https://nvd.nist.gov/vuln-metrics/cvss/v2-calculator?name=CVE-2015-2806
CVSSv3 Calc https://nvd.nist.gov/vuln-metrics/cvss/v3-calculator?name=CVE-2015-2806
Summary Stack-based buffer overflow in asn1_der_decoding in libtasn1 before 4.4 allows
remote attackers to have unspecified impact via unknown vectors.
Source https://nvd.nist.gov/vuln/detail/CVE-2015-2806
RHEL-CVE https://access.redhat.com/security/cve/CVE-2015-2806
CWE-119 (nvd) https://cwe.mitre.org/data/definitions/119.html
Package/CPE libtasn1-3.8-3.el7 -
Confidence 100 / OvalMatch
... snip ...
Vuls has Terminal-Based User Interface to display the scan result.
$ vuls tui
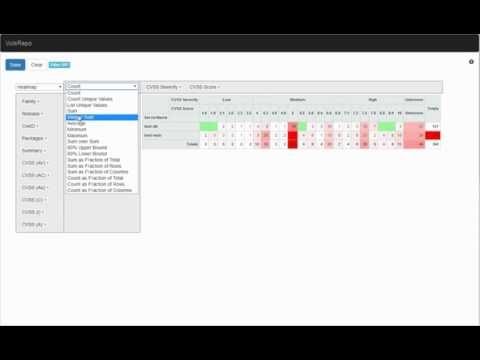
VulsRepo is a awesome Web UI for Vuls.
Check it out the Online Demo.
This tutorial will let you scan the vulnerabilities on the remote host via SSH with Vuls.
This can be done in the following steps.
- Launch new Ubuntu Linux
- Enable to SSH from localhost
- Configuration
- Check config.toml and settings on the server before scanning
- Scan
- Reporting
We will use the Vuls server (called localhost) created in the previous tutorial.
Same like as Tutorial: Local Scan Mode#Step1. Launch CentOS7
Launch a new terminal and SSH to the Remote host.
To add the remote host's Host Key to $HOME/.ssh/known_hosts, you need to log in to the remote host through SSH before scanning.
Vuls doesn't support SSH password authentication. So you have to use SSH key-based authentication.
Create a keypair on the localhost then append the public key to authorized_keys on the remote host.
- localhost
$ ssh-keygen -t rsaCopy ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub to the clipboard.
- Remote Host
$ mkdir ~/.ssh
$ chmod 700 ~/.ssh
$ touch ~/.ssh/authorized_keys
$ chmod 600 ~/.ssh/authorized_keys
$ vim ~/.ssh/authorized_keys
Paste from the clipboard to ~/.ssh/.authorized_keys
And also, confirm that the host keys of scan target servers has been registered in the known_hosts of the localhost.
To add the remote host's Host Key to $HOME/.ssh/known_hosts, you need to log in to the remote host through SSH before scanning.
- localhost
$ ssh [email protected] -i ~/.ssh/id_rsa
- localhost
$ cd $HOME
$ cat config.toml
[servers]
[servers.ubuntu]
host = "172.31.4.82"
port = "22"
user = "ubuntu"
keyPath = "/home/centos/.ssh/id_rsa"
$ vuls configtest ubuntu
$ vuls scan ubuntu
... snip ...
One Line Summary
================
ubuntu ubuntu16.04 30 updatable packages
See Tutorial: Local Scan Mode#Step9. Reporting
See Tutorial: Local Scan Mode#Step10. TUI
See Tutorial: Local Scan Mode#Step11. Web UI
see https://github.com/future-architect/vuls/tree/master/setup/docker
Deploy Vuls to the scan target server. Vuls issues a command to the local host (not via SSH). Aggregate the JSON of the scan result into another server. Since it is necessary to access the CVE database in order to refine the scan result, start go-cve-dictionary in server mode beforehand. On the aggregation server, you can refer to the scanning result of each scan target server using WebUI or TUI.
- Scan without Root Privilege
- Scan with No internet access on some OS.
| Distribution | Scan Speed | Need Root Privilege | OVAL | Need Internet Access on scan tareget |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alpine | Fast | No | Supported | Need |
| CentOS | Fast | No | Supported | No |
| RHEL | Fast | No | Supported | No |
| Oracle | Fast | No | Supported | No |
| Ubuntu | Fast | No | Supported | No |
| Debian | Fast | No | Supported | No |
| Raspbian | 1st time: Slow From 2nd time: Fast |
Need | No | Need |
| FreeBSD | Fast | No | No | Need |
| Amazon | Fast | No | No | Need |
| SUSE Enterprise | Fast | No | Supported | No |
| Distribution | Scan Speed | Need Root Privilege | OVAL | Need Internet Access on scan tareget |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alpine | Fast | No | Supported | Need |
| CentOS | Slow | No | Supported | Need |
| RHEL | Slow | Need | Supported | Need |
| Oracle | Slow | Need | Supported | Need |
| Ubuntu | 1st time: Slow From 2nd time: Fast |
Need | Supported | Need |
| Debian | 1st time: Slow From 2nd time: Fast |
Need | Supported | Need |
| Raspbian | 1st time: Slow From 2nd time: Fast |
Need | No | Need |
| FreeBSD | Fast | No | No | Need |
| Amazon | Slow | No | No | Need |
| SUSE Enterprise | Fast | No | Supported | No |
-
On Ubuntu, Debian and Raspbian Vuls issues
apt-get changelogfor each upgradable packages and parse the changelog.
apt-get changelogis slow and resource usage is heavy when there are many updatable packages on target server.
Vuls stores these changelogs to KVS(boltdb).
From the second time on, the scan speed is fast by using the local cache. -
On CentOS Vuls issues
yum changelogto get changelogs of upgradable packages at once and parse the changelog. -
On RHEL, Oracle, Amazon and FreeBSD Detect CVE IDs by using package manager.
-
On SUSE Enterprise Linux and Alpine Linux Same as fast scan mode for now.
web/app server in the same configuration under the load balancer
If there is a staging environment with the same configuration as the production environment, you can scan the server in staging environment
| Distribution | Release |
|---|---|
| Alpine | 3.2 and later |
| Ubuntu | 14, 16 |
| Debian | 7, 8, 9 |
| RHEL | 5, 6, 7 |
| Oracle Linux | 5, 6, 7 |
| CentOS | 6, 7 |
| Amazon Linux | All |
| FreeBSD | 10, 11 |
| SUSE Enterprise | 11, 12 |
| Raspbian | Jessie, Stretch |
Discovery subcommand discovers active servers specified in CIDR range, then display the template of config file(TOML format) to terminal.
$ vuls discover -help
discover:
discover 192.168.0.0/24
$ vuls discover 172.31.4.0/24
# Create config.toml using below and then ./vuls --config=/path/to/config.toml
[slack]
hookURL = "https://hooks.slack.com/services/abc123/defghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz"
#legacyToken = "xoxp-11111111111-222222222222-3333333333"
channel = "#channel-name"
#channel = "${servername}"
iconEmoji = ":ghost:"
authUser = "username"
notifyUsers = ["@username"]
[email]
smtpAddr = "smtp.gmail.com"
smtpPort = "587"
user = "username"
password = "password"
from = "[email protected]"
to = ["[email protected]"]
cc = ["[email protected]"]
subjectPrefix = "[vuls]"
[default]
#port = "22"
#user = "username"
#keyPath = "/home/username/.ssh/id_rsa"
#cpeNames = [
# "cpe:/a:rubyonrails:ruby_on_rails:4.2.1",
#]
#ignoreCves = ["CVE-2016-6313"]
#optional = [
# ["key", "value"],
#]
[servers]
[servers.172-31-4-82]
host = "172.31.4.82"
#port = "22"
#user = "root"
#keyPath = "/home/username/.ssh/id_rsa"
#type = "pseudo"
#cpeNames = [
# "cpe:/a:rubyonrails:ruby_on_rails:4.2.1",
#]
#ignoreCves = ["CVE-2016-6313"]
#optional = [
# ["key", "value"],
#]
#[servers.172-31-4-82.containers]
#type = "lxd" # or "docker" or "lxc"
#includes = ["${running}"]
#excludes = ["container_name", "container_id"]
You can customize your configuration using this template.
-
Slack section
[slack] hookURL = "https://hooks.slack.com/services/abc123/defghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz" #legacyToken = "xoxp-11111111111-222222222222-3333333333" channel = "#channel-name" #channel = "${servername}" iconEmoji = ":ghost:" authUser = "username" notifyUsers = ["@username"]-
hookURL or legacyToken.
If there are a lot of vulnerabilities, it is better to use legacyToken since the Slack notification will be flooded.-
hookURL : Incoming webhook's URL (hookURL is ignored when legacyToken is set.)

-
legacyToken : slack legacy token (https://api.slack.com/custom-integrations/legacy-tokens)

-
-
channel : channel name. If you set
${servername}to channel, the report will be sent to each channel.
In the following example, the report will be sent to the#server1and#server2.
Be sure to create these channels before scanning.[slack] channel = "${servername}" ...snip... [servers] [servers.server1] host = "172.31.4.82" ...snip... [servers.server2] host = "172.31.4.83" ...snip... -
iconEmoji: emoji
-
authUser: username of the slack team
-
notifyUsers: a list of Slack usernames to send Slack notifications. If you set
["@foo", "@bar"]to notifyUsers, @foo @bar will be included in text.
So @foo, @bar can receive mobile push notifications on their smartphone.
-
-
EMail section
[email] smtpAddr = "smtp.gmail.com" smtpPort = "587" user = "username" password = "password" from = "[email protected]" to = ["[email protected]"] cc = ["[email protected]"] subjectPrefix = "[vuls]" -
Default section
[default] #port = "22" #user = "username" #keyPath = "/home/username/.ssh/id_rsa" #cpeNames = [ # "cpe:/a:rubyonrails:ruby_on_rails:4.2.1", #] #ignoreCves = ["CVE-2016-6313"] #optional = [ # ["key", "value"], #]Items of the default section will be used if not specified.
-
servers section
[servers] [servers.172-31-4-82] host = "172.31.4.82" #port = "22" #user = "root" #keyPath = "/home/username/.ssh/id_rsa" #type = "pseudo" #cpeNames = [ # "cpe:/a:rubyonrails:ruby_on_rails:4.2.1", #] #ignoreCves = ["CVE-2016-6314"] #optional = [ # ["key", "value"], #] #[servers.172-31-4-82.containers] #type = "lxd" # or "docker" or "lxc" #includes = ["${running}"] #excludes = ["container_name", "container_id"]You can overwrite the default value specified in default section.
- host: IP address or hostname of target server
- port: SSH Port number
- user: SSH username
- keyPath: SSH private key path
- type: "pseudo" for non-ssh scanning. see #531
- cpeNames: see Usage: Scan vulnerability of non-OS package
- ignoreCves: CVE IDs that will not be reported. But output to JSON file.
- optional: Add additional information to JSON report.
- containers: see [Example: Scan containers (Docker/LXD/LXC)(#example-scan-containers-dockerlxdlxc)
Vuls supports two types of SSH. One is external command. The other is native go implementation. For details, see -ssh-native-insecure option
Multiple SSH authentication methods are supported.
- SSH agent
- SSH public key authentication (with password and empty password) Password authentication is not supported.
$ vuls configtest --help
configtest:
configtest
[-deep]
[-config=/path/to/config.toml]
[-log-dir=/path/to/log]
[-ask-key-password]
[-ssh-native-insecure]
[-containers-only]
[-timeout=300]
[-debug]
[SERVER]...
-ask-key-password
Ask ssh privatekey password before scanning
-config string
/path/to/toml (default "/Users/kotakanbe/go/src/github.com/future-architect/vuls/config.toml")
-containers-only
Test containers only. Default: Test both of hosts and containers
-debug
debug mode
-deep
Config test for deep scan mode
-http-proxy string
http://proxy-url:port (default: empty)
-log-dir string
/path/to/log (default "/var/log/vuls")
-ssh-native-insecure
Use Native Go implementation of SSH. Default: Use the external command
-timeout int
Timeout(Sec) (default 300)
The configtest subcommand checks whether vuls is able to connect via SSH to servers/containers defined in the config.toml
| Distribution | Release | Requirements |
|---|---|---|
| Alpine | 3.2 and later | - |
| Ubuntu | 12, 14, 16 | - |
| Debian | 7, 8, 9 | reboot-notifier |
| CentOS | 6, 7 | - |
| Amazon | All | yum-utils |
| RHEL | 5, 6, 7 | - |
| Oracle Linux | 5, 6, 7 | - |
| SUSE Enterprise | 11, 12 | - |
| FreeBSD | 10, 11 | - |
| Raspbian | Jessie, Stretch | - |
Some dependent packages are needed in Deep Scan Mode. The configtest subcommand with --deep flag checks whether the packages are installed on the scan target server and also check /etc/sudoers
In order to scan with deep scan mode, the following dependencies are required, so you need to install them manually or with tools such as Ansible.
| Distribution | Release | Requirements |
|---|---|---|
| Alpine | 3.2 and later | - |
| Ubuntu | 12, 14, 16 | - |
| Debian | 7, 8, 9 | aptitude, reboot-notifier |
| CentOS | 6, 7 | yum-utils, yum-plugin-changelog |
| Amazon | All | yum-utils, yum-plugin-changelog |
| RHEL | 5 | yum-utils, yum-changelog, yum-security |
| RHEL | 6 | yum-utils, yum-plugin-changelog, yum-plugin-security |
| RHEL | 7 | yum-utils, yum-plugin-changelog |
| Oracle Linux | 5 | yum-utils, yum-changelog, yum-security |
| Oracle Linux | 6 | yum-utils, yum-plugin-changelog, yum-plugin-security |
| Oracle Linux | 7 | yum-utils, yum-plugin-changelog |
| SUSE Enterprise | 11, 12 | - |
| FreeBSD | 10 | - |
| Raspbian | Wheezy, Jessie | - |
The configtest subcommand also checks sudo settings on target servers whether Vuls is able to SUDO with nopassword via SSH. And if you run Vuls without -ssh-native-insecure option, requiretty must be defined in /etc/sudoers.
Defaults:vuls !requiretty
For details, see -ssh-native-insecure option
Example of /etc/sudoers on target servers
- RHEL 5 / Oracle Linux 5
vuls ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD:/usr/bin/yum --color=never repolist, /usr/bin/yum --color=never list-security --security, /usr/bin/yum --color=never info-security, /usr/bin/repoquery, /usr/bin/yum --color=never changelog all *
Defaults:vuls env_keep="http_proxy https_proxy HTTP_PROXY HTTPS_PROXY"
- RHEL 6, 7 / Oracle Linux 6, 7
vuls ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD:/usr/bin/yum --color=never repolist, /usr/bin/yum --color=never --security updateinfo list updates, /usr/bin/yum --color=never --security updateinfo updates, /usr/bin/repoquery, /usr/bin/yum --color=never changelog all *
Defaults:vuls env_keep="http_proxy https_proxy HTTP_PROXY HTTPS_PROXY"
- Debian/Ubuntu/Raspbian
vuls ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD: /usr/bin/apt-get update
Defaults:vuls env_keep="http_proxy https_proxy HTTP_PROXY HTTPS_PROXY"
- On CentOS, Amazon Linux, SUSE Enterprise, FreeBSD, it is possible to scan without root privilege for now.
$ vuls scan -help
scan:
scan
[-deep]
[-config=/path/to/config.toml]
[-results-dir=/path/to/results]
[-log-dir=/path/to/log]
[-cachedb-path=/path/to/cache.db]
[-ssh-native-insecure]
[-containers-only]
[-skip-broken]
[-http-proxy=http://192.168.0.1:8080]
[-ask-key-password]
[-timeout=300]
[-timeout-scan=7200]
[-debug]
[-pipe]
[SERVER]...
-ask-key-password
Ask ssh privatekey password before scanning
-cachedb-path string
/path/to/cache.db (local cache of changelog for Ubuntu/Debian)
-config string
/path/to/toml
-containers-only
Scan containers only. Default: Scan both of hosts and containers
-debug
debug mode
-deep
Deep scan mode. Scan accuracy improves and information becomes richer. Since analysis of changelog, issue commands requiring sudo, but it may be slower and high load on the scan tareget server.
-http-proxy string
http://proxy-url:port (default: empty)
-log-dir string
/path/to/log (default "/var/log/vuls")
-pipe
Use stdin via PIPE
-results-dir string
/path/to/results
-skip-broken
[For CentOS] yum update changelog with --skip-broken option
-ssh-native-insecure
Use Native Go implementation of SSH. Default: Use the external command
-timeout int
Number of seconds for processing other than scan (default 300)
-timeout-scan int
Number of second for scaning vulnerabilities for all servers (default 7200)
You need to execute vuls configtest --deep to check the configuration of the target server before scanning with -deep flag.
For details about deep scan mode, see below.
Vuls supports different types of SSH.
By Default, external SSH command will be used.
This is useful If you want to use ProxyCommand or cipher algorithm of SSH that is not supported by native go implementation.
Don't forget to add below line to /etc/sudoers on the target servers. (username: vuls)
Defaults:vuls !requiretty
To use native Go implementation from crypto/ssh, specify this option.
This is useful in situations where you may not have access to traditional UNIX tools.
But it is important to note that this mode does not check the host key.
| SSH key password | -ask-key-password | |
|---|---|---|
| empty password | - | |
| with password | required | or use ssh-agent |
$ vuls scan -ask-key-password
With this sample command, it will ..
- Ask SSH key password before scanning
- Scan all servers defined in config file
$ vuls scan server1 server2
With this sample command, it will ..
- Use SSH Key-Based authentication with empty password (without -ask-key-password option)
- Scan only 2 servers (server1, server2)
Vuls scans localhost instead of SSH if the host address is localhst or 127.0.0.1 and the port is local in config.
For more details, see Architecture section
- config.toml
[servers] [servers.localhost] host = "localhost" # or "127.0.0.1" port = "local"
If you use local scan mode for cron jobs, don't forget to add below line to /etc/sudoers on RHEL/CentOS. (username: vuls)
Defaults:vuls !requiretty
It is common that keep containers running without SSHd daemon.
see Docker Blog:Why you don't need to run SSHd in your Docker containers
Vuls scans Docker containers via docker exec instead of SSH.
For more details, see Architecture section
-
To scan all of running containers
"${running}"needs to be set in the containers item.[servers] [servers.172-31-4-82] host = "172.31.4.82" user = "ec2-user" keyPath = "/home/username/.ssh/id_rsa" [servers.172-31-4-82.containers] includes = ["${running}"] -
To scan specific containers
The container ID or container name needs to be set in the containers item.
In the following example, onlycontainer_name_aand4aa37a8b63b9will be scanned.
Be sure to check these containers are running state before scanning.
If specified containers are not running, Vuls gives up scanning with printing error message.[servers] [servers.172-31-4-82] host = "172.31.4.82" user = "ec2-user" keyPath = "/home/username/.ssh/id_rsa" [servers.172-31-4-82.containers] includes = ["container_name_a", "4aa37a8b63b9"] -
To scan except specific containers
[servers] [servers.172-31-4-82] host = "172.31.4.82" user = "ec2-user" keyPath = "/home/username/.ssh/id_rsa" [servers.172-31-4-82.containers] includes = ["${running}"] excludes = ["container_name_a", "4aa37a8b63b9"] -
To scan containers only
- --containers-only option is available.
Vuls scans lxd via lxc exec instead of SSH.
[servers]
[servers.172-31-4-82]
host = "172.31.4.82"
user = "ec2-user"
keyPath = "/home/username/.ssh/id_rsa"
[servers.172-31-4-82.containers]
type = "lxd"
includes = ["${running}"]
Vuls scans lxc via lxc-attach instead of SSH.
[servers]
[servers.172-31-4-82]
host = "172.31.4.82"
user = "ec2-user"
keyPath = "/home/username/.ssh/id_rsa"
[servers.172-31-4-82.containers]
type = "lxc"
includes = ["${running}"]
LXC required root privilege.
Example of /etc/sudoers on target servers
vuls ALL=(ALL) NOPASSWD:/usr/bin/lxc-attach -n *, /usr/bin/lxc-ls *
report:
report
[-lang=en|ja]
[-config=/path/to/config.toml]
[-results-dir=/path/to/results]
[-log-dir=/path/to/log]
[-refresh-cve]
[-cvedb-type=sqlite3|mysql|postgres]
[-cvedb-path=/path/to/cve.sqlite3]
[-cvedb-url=http://127.0.0.1:1323 DB connection string]
[-ovaldb-type=sqlite3|mysql]
[-ovaldb-path=/path/to/oval.sqlite3]
[-ovaldb-url=http://127.0.0.1:1324 or DB connection string]
[-cvss-over=7]
[-diff]
[-ignore-unscored-cves]
[-ignore-unfixed]
[-to-email]
[-to-slack]
[-to-localfile]
[-to-s3]
[-to-azure-blob]
[-format-json]
[-format-xml]
[-format-one-email]
[-format-one-line-text]
[-format-short-text]
[-format-full-text]
[-gzip]
[-aws-profile=default]
[-aws-region=us-west-2]
[-aws-s3-bucket=bucket_name]
[-aws-s3-results-dir=/bucket/path/to/results]
[-azure-account=accout]
[-azure-key=key]
[-azure-container=container]
[-http-proxy=http://192.168.0.1:8080]
[-debug]
[-debug-sql]
[-pipe]
[RFC3339 datetime format under results dir]
-aws-profile string
AWS profile to use (default "default")
-aws-region string
AWS region to use (default "us-east-1")
-aws-s3-bucket string
S3 bucket name
-aws-s3-results-dir string
/bucket/path/to/results (option)
-azure-account string
Azure account name to use. AZURE_STORAGE_ACCOUNT environment variable is used if not specified
-azure-container string
Azure storage container name
-azure-key string
Azure account key to use. AZURE_STORAGE_ACCESS_KEY environment variable is used if not specified
-config string
/path/to/toml
-cvedb-path string
/path/to/sqlite3 (For get cve detail from cve.sqlite3)
-cvedb-type string
DB type for fetching CVE dictionary (sqlite3, mysql or postgres) (default "sqlite3")
-cvedb-url string
http://cve-dictionary.com:8080 DB connection string
-cvss-over float
-cvss-over=6.5 means reporting CVSS Score 6.5 and over (default: 0 (means report all))
-diff
Difference between previous result and current result
-debug
debug mode
-debug-sql
SQL debug mode
-format-full-text
Detail report in plain text
-format-json
JSON format
-format-one-email
Send all the host report via only one EMail (Specify with -to-email)
-format-one-line-text
One line summary in plain text
-format-short-text
Summary in plain text
-format-xml
XML format
-gzip
gzip compression
-http-proxy string
http://proxy-url:port (default: empty)
-ignore-unscored-cves
Don't report the unscored CVEs
-ignore-unfixed
Don't report the unfixed CVEs
-lang string
[en|ja] (default "en")
-log-dir string
/path/to/log (default "/var/log/vuls")
-ovaldb-path string
/path/to/sqlite3 (For get oval detail from oval.sqlite3) (default "/Users/kotakanbe/go/src/github.com/future-architect/vuls/oval.sqlite3")
-ovaldb-type string
DB type for fetching OVAL dictionary (sqlite3 or mysql) (default "sqlite3")
-ovaldb-url string
http://goval-dictionary.com:1324 or mysql connection string
-pipe
Use stdin via PIPE
-refresh-cve
Refresh CVE information in JSON file under results dir
-results-dir string
/path/to/results
-to-azure-blob
Write report to Azure Storage blob (container/yyyyMMdd_HHmm/servername.json/xml/txt)
-to-email
Send report via Email
-to-localfile
Write report to localfile
-to-s3
Write report to S3 (bucket/dir/yyyyMMdd_HHmm/servername.json/xml/txt)
-to-slack
Send report via Slack
$ vuls report -format-full-text
172-31-4-82 (amazon 2015.09)
============================
Total: 94 (High:19 Medium:54 Low:7 ?:14) 103 updatable packages
CVE-2016-5636
-------------
Score 10.0 (High)
Vector (AV:N/AC:L/Au:N/C:C/I:C/A:C)
Summary Integer overflow in the get_data function in zipimport.c in CPython (aka Python)
before 2.7.12, 3.x before 3.4.5, and 3.5.x before 3.5.2 allows remote attackers
to have unspecified impact via a negative data size value, which triggers a
heap-based buffer overflow.
CWE https://cwe.mitre.org/data/definitions/190.html
NVD https://web.nvd.nist.gov/view/vuln/detail?vulnId=CVE-2016-5636
MITRE https://cve.mitre.org/cgi-bin/cvename.cgi?name=CVE-2016-5636
CVE Details http://www.cvedetails.com/cve/CVE-2016-5636
CVSS Calculator https://nvd.nist.gov/cvss/v2-calculator?name=CVE-2016-5636&vector=(AV:N/AC:L/...
RHEL-CVE https://access.redhat.com/security/cve/CVE-2016-5636
ALAS-2016-724 https://alas.aws.amazon.com/ALAS-2016-724.html
Package python27-2.7.10-4.119.amzn1 -> python27-2.7.12-2.120.amzn1
python27-devel-2.7.10-4.119.amzn1 -> python27-devel-2.7.12-2.120.amzn1
python27-libs-2.7.10-4.119.amzn1 -> python27-libs-2.7.12-2.120.amzn1
Confidence 100 / YumUpdateSecurityMatch
... snip ...
cent6 (centos6.6)
=================
Total: 145 (High:23 Medium:101 Low:21 ?:0) 83 updatable packages
cent6means that it is a scan report ofservers.cent6defined in cocnfig.toml.(centos6.6)means that the version of the OS is CentOS6.6.Total: 145 (High:23 Medium:101 Low:21 ?:0)means that a total of 145 vulnerabilities exist, and the distribution of CVSS Severity is displayed.83 updatable packagesmeans that there are 83 updateable packages on the target server.
CVE-2016-0702
----------------
Max Score 2.6 IMPORTANT (redhat)
nvd 1.9/AV:L/AC:M/Au:N/C:P/I:N/A:N
redhat 2.6/AV:L/AC:H/Au:N/C:P/I:P/A:N
jvn 1.9/AV:L/AC:M/Au:N/C:P/I:N/A:N
CVSSv2 Calc https://nvd.nist.gov/vuln-metrics/cvss/v2-calculator?name=CVE-2016-0702
Summary The MOD_EXP_CTIME_COPY_FROM_PREBUF function in crypto/bn/bn_exp.c in OpenSSL
1.0.1 before 1.0.1s and 1.0.2 before 1.0.2g does not properly consider
cache-bank access times during modular exponentiation, which makes it easier for
local users to discover RSA keys by running a crafted application on the same
Intel Sandy Bridge CPU core as a victim and leveraging cache-bank conflicts, aka
a "CacheBleed" attack.
Source https://nvd.nist.gov/vuln/detail/CVE-2016-0702
RHEL-CVE https://access.redhat.com/security/cve/CVE-2016-0702
CWE-200 (nvd) https://cwe.mitre.org/data/definitions/200.html
Package/CPE openssl-1.0.1e-30.el6 - 1.0.1e-57.el6
Confidence 100 / OvalMatch
-
Max Scoremeans Max CVSS Score. -
nvdshows CVSS Vector of NVD -
redhatshows CVSS Vector of RedHat OVAL -
jvnshows CVSS Vector of JVN -
Summarymeans Summary of the CVE. -
CWEmeans CWE - Common Weakness Enumeration of the CVE. -
Packageshows the package version information including this vulnerability. -
Confidencemeans the reliability of detection.100is highly reliableYumUpdateSecurityMatchis the method of detecting this vulnerability.
-
Item list of
ConfidenceDetection Method Confidence OS Description OvalMatch 100 CentOS, RHEL, Oracle, Ubuntu, Debian, SUSE Detection using OVAL YumUpdateSecurityMatch 100 RHEL, Amazon, Oracle Detection using yum-plugin-security ChangelogExactMatch 95 CentOS, Ubuntu, Debian, Raspbian Exact version match between changelog and package version ChangelogLenientMatch 50 Ubuntu, Debian, Raspbian Lenient version match between changelog and package version PkgAuditMatch 100 FreeBSD Detection using pkg audit CpeNameMatch 100 All Search for NVD information with CPE name specified in config.toml
$ vuls report \
-to-slack \
-cvss-over=7 \
-cvedb-path=$PWD/cve.sqlite3
With this sample command, it will ..
- Send scan results to slack
- Only Report CVEs that CVSS score is over 7
$ vuls report \
-to-slack \
-cvss-over=7 \
-cvedb-path=$PWD/cve.sqlite3
With this sample command, it will ..
- Send scan results to slack
- Only Report CVEs that CVSS score is over 7
To put results in S3 bucket, configure following settings in AWS before reporting.
- Create S3 bucket. see Creating a Bucket
- Configure access to S3 resources. You can do this in several ways:
- Configure the environment variables. see Configuring the AWS Command Line Interface
- Configure the security credentials. see Configuring the AWS Command Line Interface
- Create an IAM role for the service and attach it to the service(EC2, AWS Lambda). Creating a Role to Delegate Permissions to an AWS Service
- To configure environment variables, security credentials, create an access key. see Managing Access Keys for IAM Users
Example of IAM policy:
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"s3:ListAllMyBuckets"
],
"Resource": "arn:aws:s3:::*"
},
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"s3:PutObject"
],
"Resource": "arn:aws:s3:::vuls/*"
}
]
}
$ vuls report \
-cvedb-path=$PWD/cve.sqlite3 \
-to-s3 \
-format-json \
-aws-region=ap-northeast-1 \
-aws-s3-bucket=vuls \
-aws-profile=default
With this sample command, it will ..
- Put scan result(JSON) in S3 bucket. The bucket name is "vuls" in ap-northeast-1 and profile is "default"
To put results in Azure Blob Storage, configure following settings in Azure before reporting.
- Create a Azure Blob container
$ vuls scan \
-cvedb-path=$PWD/cve.sqlite3 \
-report-azure-blob \
-azure-container=vuls \
-azure-account=test \
-azure-key=access-key-string
With this sample command, it will ..
- Put scan result(JSON) in Azure Blob Storage. The container name is "vuls", storage account is "test" and accesskey is "access-key-string"
account and access key can be defined in environment variables.
$ export AZURE_STORAGE_ACCOUNT=test
$ export AZURE_STORAGE_ACCESS_KEY=access-key-string
$ vuls scan \
-cvedb-path=$PWD/cve.sqlite3 \
-report-azure-blob \
-azure-container=vuls
Define ignoreCves in config if you don't want to report(Slack, EMail, Text...) specific CVE IDs. But these ignoreCves will be output to JSON file like below.
- config.toml
[default]
ignoreCves = ["CVE-2016-6313"]
[servers.bsd]
host = "192.168.11.11"
user = "kanbe"
ignoreCves = ["CVE-2016-6314"]- bsd.json
[
{
"ServerName": "bsd",
"Family": "FreeBSD",
"Release": "10.3-RELEASE",
"IgnoredCves" : [
"CveDetail" : {
"CVE-2016-6313",
...
},
"CveDetail" : {
"CVE-2016-6314",
...
}
]
}
]Optional key-value can be outputted to JSON.
The key-value in the default section will be overwritten by servers section's key-value.
For instance, you can use this field for Azure ResourceGroup name, Azure VM Name and so on.
- config.toml
[default]
optional = [
["key1", "default_value"],
["key3", "val3"],
]
[servers.bsd]
host = "192.168.11.11"
user = "kanbe"
optional = [
["key1", "val1"],
["key2", "val2"],
]- bsd.json
[
{
"ServerName": "bsd",
"Family": "FreeBSD",
"Release": "10.3-RELEASE",
.... snip ...
"Optional": [
[ "key1", "val1" ],
[ "key2", "val2" ],
[ "key3", "val3" ]
]
}
]$ vuls report \
-cvedb-type=mysql \
-cvedb-url="user:pass@tcp(localhost:3306)/dbname?parseTime=true"
$ vuls report \
-cvedb-type=postgres \
-cvedb-url=""host=myhost user=user dbname=dbname sslmode=disable password=password""
$ vuls report \
-cvedb-type=redis -cvedb-url="redis://localhost/0"
-ovaldb-type=redis -ovaldb-url="redis://localhost/1"
It is possible to detect vulnerabilities in non-OS packages, such as something you compiled by yourself, language libraries and frameworks, that have been registered in the CPE.
-
How to search CPE name by software name
-
NVD: Search Common Platform Enumerations (CPE)
Check CPE Naming Format: 2.2 -
go-cpe-dictionary is a good choice for geeks.
You can search a CPE name by the application name incrementally.
-
-
Configuration
To detect the vulnerability of Ruby on Rails v4.2.1, cpeNames needs to be set in the servers section.[servers] [servers.172-31-4-82] host = "172.31.4.82" user = "ec2-user" keyPath = "/home/username/.ssh/id_rsa" cpeNames = [ "cpe:/a:rubyonrails:ruby_on_rails:4.2.1", ] -
type="pseudo" Specify this when you want to detect vulnerability by specifying cpename without SSH connection. The pseudo type does not do anything when scanning. Search for NVD at report time and detect vulnerability of software specified as cpenamae.
[servers] [servers.172-31-4-82] type = "pseudo" cpeNames = [ "cpe:/a:rubyonrails:ruby_on_rails:4.2.1", ]
Usage: Integrate with OWASP Dependency Check to Automatic update when the libraries are updated (Experimental)
OWASP Dependency check is a utility that identifies project dependencies and checks if there are any known, publicly disclosed, vulnerabilities.
Benefit of integrating Vuls And OWASP Dependency Check is below.
- Automatic Update of Vuls config when the libraries are updated.
- Reporting by Email or Slack by using Vuls.
- Reporting in Japanese
- OWASP Dependency Check supports only English
How to integrate Vuls with OWASP Dependency Check
-
Execute OWASP Dependency Check with --format=XML option.
-
Define the xml file path of dependency check in config.toml.
[servers] [servers.172-31-4-82] host = "172.31.4.82" user = "ec2-user" keyPath = "/home/username/.ssh/id_rsa" dependencyCheckXMLPath = "/tmp/dependency-check-report.xml"
tui:
tui
[-refresh-cve]
[-cvedb-type=sqlite3|mysql|postgres]
[-cvedb-path=/path/to/cve.sqlite3]
[-cvedb-url=http://127.0.0.1:1323 DB connection string]
[-ovaldb-type=sqlite3|mysql]
[-ovaldb-path=/path/to/oval.sqlite3]
[-ovaldb-url=http://127.0.0.1:1324 or DB connection string]
[-cvss-over=7]
[-ignore-unscored-cves]
[-ignore-unfixed]
[-refresh-cve]
[-results-dir=/path/to/results]
[-log-dir=/path/to/log]
[-debug]
[-debug-sql]
[-pipe]
-cvedb-path string
/path/to/sqlite3 (For get cve detail from cve.sqlite3)
-cvedb-type string
DB type for fetching CVE dictionary (sqlite3, mysql or postgres) (default "sqlite3")
-cvedb-url string
http://cve-dictionary.com:8080 DB connection string
-ovaldb-path string
/path/to/sqlite3 (For get oval detail from oval.sqlite3) (default "/Users/kotakanbe/go/src/github.com/future-architect/vuls/oval.sqlite3")
-ovaldb-type string
DB type for fetching OVAL dictionary (sqlite3 or mysql) (default "sqlite3")
-ovaldb-url string
http://goval-dictionary.com:1324 or mysql connection string
-cvss-over float
-cvss-over=6.5 means reporting CVSS Score 6.5 and over (default: 0 (means report all))
-ignore-unfixed
Don't report the unfixed CVEs
-ignore-unscored-cves
Don't report the unscored CVEs
-debug
debug mode
-debug-sql
debug SQL
-log-dir string
/path/to/log (default "/var/log/vuls")
-pipe
Use stdin via PIPE
-refresh-cve
Refresh CVE information in JSON file under results dir
-results-dir string
/path/to/results
Key binding is below.
| key | |
|---|---|
| TAB | move cursor among the panes |
| Arrow up/down | move cursor to up/down |
| Ctrl+j, Ctrl+k | move cursor to up/down |
| Ctrl+u, Ctrl+d | page up/down |
For details, see https://github.com/future-architect/vuls/blob/master/report/tui.go
- Display the list of scan results.
$ vuls history
2016-12-30T10:34:38+09:00 1 servers: u16
2016-12-28T19:15:19+09:00 1 servers: ama
2016-12-28T19:10:03+09:00 1 servers: cent6
- Display the result of scan 2016-12-30T10:34:38+09:00
$ vuls tui 2016-12-30T10:34:38+09:00
$ vuls history | peco | vuls tui -pipe
Run go-cve-dictionary as server mode before scanning on 192.168.10.1
$ go-cve-dictionary server -bind=192.168.10.1 -port=1323
Run Vuls with -cvedb-url option.
$ vuls report -cvedb-url=http://192.168.0.1:1323
see go-cve-dictionary#usage-fetch-nvd-data
$ goval-dictionary server -bind=192.168.10.1 -port=1324
Run Vuls with -ovaldb-url option.
$ vuls report -ovaldb-url=http://192.168.0.1:1323
- Update go-cve-dictionary
If the DB schema was changed, please specify new SQLite3, MySQL, PostgreSQL or Redis DB file.
$ cd $GOPATH/src/github.com/kotakanbe/go-cve-dictionary
$ git pull
$ rm -r vendor
$ make install
- Update goval-dictionary
If the DB schema was changed, please specify new SQLite3, MySQL, PostgreSQL or Redis DB file.
$ cd $GOPATH/src/github.com/kotakanbe/goval-dictionary
$ git pull
$ rm -r vendor
$ make install
- Update vuls
$ cd $GOPATH/src/github.com/future-architect/vuls
$ git pull
$ rm -r vendor
$ make install
- Binary file was built under $GOPATH/bin
- If an error occurs, delete
$GOPATH/pkgbefore executing it
-
Unable to go get vuls
Update git to the latest version. Old version of git can't get some repositories.
see https://groups.google.com/forum/#!topic/mgo-users/rO1-gUDFo_g -
HTTP Proxy Support
If your system is behind HTTP proxy, you have to specify --http-proxy option. -
How to Daemonize go-cve-dictionary
Use Systemd, Upstart or supervisord, daemontools... -
How to Enable Automatic-Update of Vulnerability Data.
Use job scheduler like Cron (with -last2y option). -
How to Enable Automatic-Scan.
Use job scheduler like Cron.
Set NOPASSWORD option in /etc/sudoers on target servers.
Use SSH Key-Based Authentication with no passphrase or ssh-agent. -
How to cross compile
$ cd /path/to/your/local-git-reporsitory/vuls $ GOOS=linux GOARCH=amd64 go build -o vuls.amd64 -
Logging
Log is under /var/log/vuls/ -
Debug
Run with --debug, --sql-debug option. -
Adjusting Open File Limit
Riak docs is awesome. -
Does Vuls accept SSH connections with fish-shell or old zsh as the login shell?
No, Vuls needs a user on the server for bash login. see also #8
Yes, fixed in #545 -
Windows
Use Microsoft Baseline Security Analyzer. MBSA
-
k1LoW/ssh_config_to_vuls_config
ssh_config to vuls config TOML format -
usiusi360/vulsrepo
VulsRepo is visualized based on the json report output in vuls.
Youtube
kotakanbe (@kotakanbe) created vuls and these fine people have contributed.
- fork a repository: github.com/future-architect/vuls to github.com/you/repo
- get original code: go get github.com/future-architect/vuls
- work on original code
- add remote to your repo: git remote add myfork https://github.com/you/repo.git
- push your changes: git push myfork
- create a new Pull Request
Please see CHANGELOG.
Please see LICENSE.