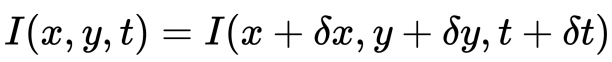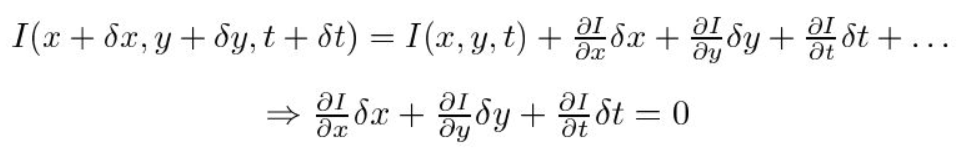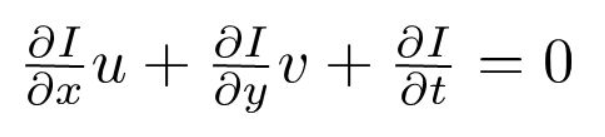cd ~
pip3 install numpy pandas
pip3 install matplotlib pillow imutils
pip3 install opencv-python
pip3 install opencv-contrib-python
git clone https://github.com/rkuo2000/cv2
cd cv2
python3 jpg_read.py
import cv2
import sys
if len(sys.argv)>1:
filename = sys.argv[1]
else:
filename = 'test.jpg'
img = cv2.imread(filename)
print(type(img))
print(img.shape)
cv2.imshow('Image',img)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.DestroyAllWindows()
python3 cam.py
import cv2
import sys
if len(sys.argv) >1:
vid = int(sys.argv[1])
else:
vid = 0
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(vid)
#cap.set(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_WIDTH,1280);
#cap.set(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_HEIGHT,720);
while(cap.isOpened()):
ret, frame = cap.read()
print(frame.shape)
#frame = cv2.flip(frame, 1) # 0: vertical flip, 1: horizontal flip
cv2.imshow('Camera', frame)
if cv2.waitKey(10) & 0xFF == ord('q'):
break
cap.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
python3 video.py
# Usage: python3 video.py filename.mp4
import sys
import cv2
import numpy as np
if len(sys.argv)>1:
if sys.argv[1].isdigit():
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(int(sys.argv[1])) # argv[1] = 0 or 1
else:
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(sys.argv[1]) # argv[1] = filename
else:
cap = cv2.VideoCapture('video/MOT16-03-raw.webm')
while(cap.isOpened()):
ret, frame = cap.read()
cv2.imshow("input", frame)
if cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF == ord('q'):
break
cap.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
 |
 |
-
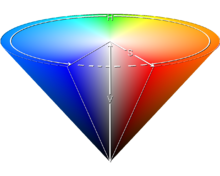
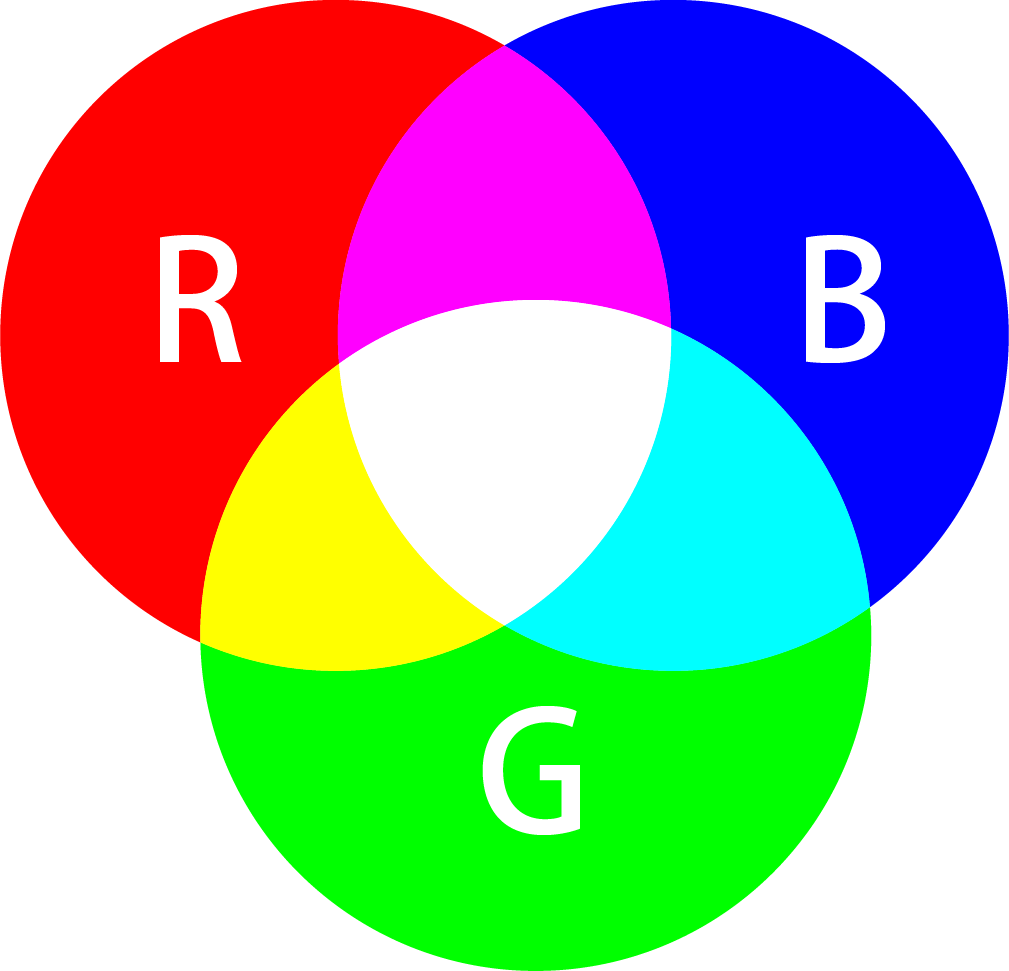
Munsell color system hue (basic color), chroma (color intensity), and value (lightness)
 |
 |
- HSL and HSV
Hue, Saturation, Lightness and Hue色調, Saturation 飽和度, Value亮度
HSV色輪允許用戶快速的選擇眾多顏色
HSV模型的圓錐表示適合於在一個單一物體中展示整個HSV色彩空間
python jpg_csc.py
import cv2
img = cv2.imread('test.jpg')
gray= cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
hsv = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2HSV)
org1= cv2.cvtColor(gray,cv2.COLOR_GRAY2BGR)
org2= cv2.cvtColor(hsv, cv2.COLOR_HSV2BGR)
cv2.imshow('ORG' ,img)
cv2.imshow('GRAY',gray)
cv2.imshow('HSV' ,hsv)
cv2.imshow('ORG1',org1)
cv2.imshow('ORG2',org2)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
python cam_object_tracking.py
import cv2
import numpy as np
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(0)
while(1):
# Take each frame
_, frame = cap.read()
# Convert BGR to HSV
hsv = cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2HSV)
# define range of blue color in HSV
lower_blue = np.array([110,50,50])
upper_blue = np.array([130,255,255])
# Threshold the HSV image to get only blue colors
mask = cv2.inRange(hsv, lower_blue, upper_blue)
# Bitwise-AND mask and original image
res = cv2.bitwise_and(frame, frame, mask=mask)
cv2.imshow('FRAME', frame)
cv2.imshow('MASK', mask)
cv2.imshow('RESULT', res)
k = cv2.waitKey(5) & 0xFF
if k==27:
break
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
python cam_skin_detection.py
python jpg_skin_detection.py
-
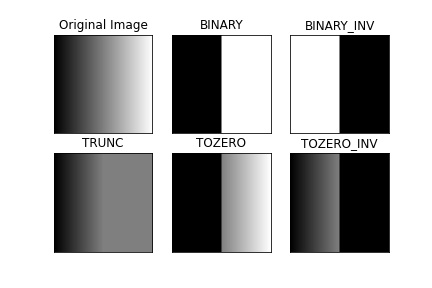
Simple Thresholding:
python jpg_image_thresholding.py- cv2.THRESH_BINARY
- cv2.THRESH_BINARY_INV
- cv2.THRESH_TRUNC
- cv2.THRESH_TOZERO
- cv2.THRESH_TOZERO_INV
- blur()
- GaussianBlur()
- medianBlur()
- bilateralFilter()
- filter2D(): jpg_2dfilter.py
python jpg_morphological_transformations.py
import cv2
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
img = cv2.imread('j.png',0)
kernel = np.ones((5,5),np.uint8)
erosion = cv2.erode(img,kernel,iterations = 1)
dilation = cv2.dilate(img,kernel,iterations = 1)
opening = cv2.morphologyEx(img, cv2.MORPH_OPEN, kernel)
closing = cv2.morphologyEx(img, cv2.MORPH_CLOSE, kernel)
gradient = cv2.morphologyEx(img, cv2.MORPH_GRADIENT, kernel)
tophat = cv2.morphologyEx(img, cv2.MORPH_TOPHAT, kernel)
blackhat = cv2.morphologyEx(img, cv2.MORPH_BLACKHAT, kernel)
titles = ['Image','Erosion','Dilation','Opening','Closing','Gradient','Tophat','Blackhat']
images = [img, erosion, dilation, opening, closing, gradient, tophat, blackhat]
for i in range(8):
plt.subplot(2,4,i+1), plt.imshow(images[i],'gray')
plt.title(titles[i])
plt.xticks([]),plt.yticks([])
plt.show()
- Scaling (Resize): jpg_resize.py
- Rotation : jpg_rotation.py
- Affine Transform: jpg_affine_transformation.py
- Perspective Transform jpg_perspective_transformation.py
Reference: OpenCV學習筆記】之仿射變換(Affine Transformation)
python jpg_sobel.py
import cv2
org = cv2.imread('test.jpg')
gray = cv2.cvtColor(org, cv2.COLOR_RGB2GRAY)
img = cv2.GaussianBlur(gray, (3,3), 0) # remove noise
# convolute with proper kernels
laplacian = cv2.Laplacian(img, cv2.CV_64F)
sobel_x = cv2.Sobel(img, cv2.CV_16S, 1, 0, ksize=5)
sobel_y = cv2.Sobel(img, cv2.CV_16S, 0, 1, ksize=5)
cv2.imshow('Laplacian', laplacian)
cv2.imshow('SobelX', sobel_x)
cv2.imshow('SobelY', sobel_y)
abs_grad_x = cv2.convertScaleAbs(sobel_x)
abs_grad_y = cv2.convertScaleAbs(sobel_y)
grad = cv2.addWeighted(abs_grad_x, 0.5, abs_grad_y, 0.5, 0)
cv2.imshow('Sobel', grad)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
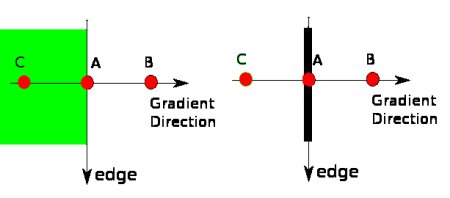
- Why Laplacian/Sobel is a High Pass Filter?
From image, you can see what frequency region each kernel blocks, and what region it passes. From that information, we can say why each kernel is a HPF or a LPF
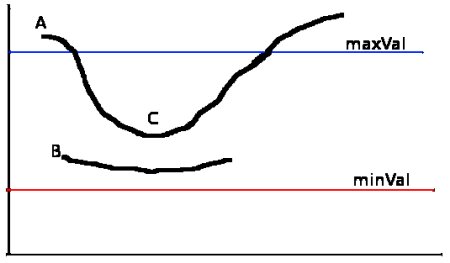
- Noise Reduction : To remove the noise in the image with a 5x5 Gaussian filter.
- Finding Intensity Gradient of the Image

- Non-maximum Suppression
- Hysteresis Thresholding
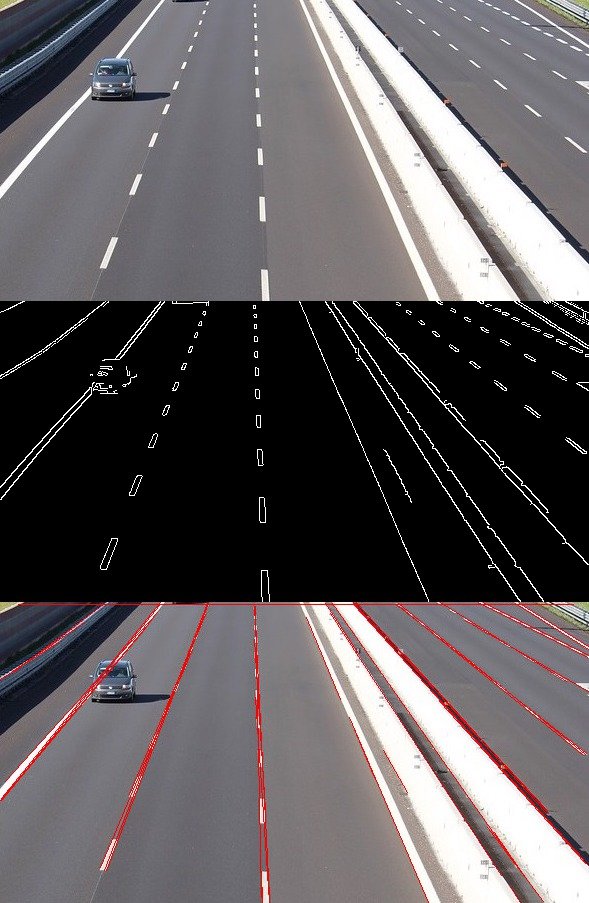
python jpg_houghlines.py
img = cv2.imread('lanes.jpg', cv2.IMREAD_COLOR) # road.png is the filename
gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
edges = cv2.Canny(gray, 50, 200)
# Detect points that form a line
lines = cv2.HoughLinesP(edges, 1, np.pi/180, max_slider, minLineLength=10, maxLineGap=250)
# Draw lines on the image
for line in lines:
x1, y1, x2, y2 = line[0]
cv2.line(img, (x1, y1), (x2, y2), (255, 0, 0), 3)
cv2.imshow("Result Image", img)
python jpg_houghcircles.py
img = cv2.imread('circles.png', cv2.IMREAD_COLOR)
gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
img_blur = cv2.medianBlur(gray, 5)
circles = cv2.HoughCircles(img_blur, cv2.HOUGH_GRADIENT, 1, img.shape[0]/64, param1=200, param2=10, minRadius=5, maxRadius=30)
# Draw detected circles
if circles is not None:
circles = np.uint16(np.around(circles))
for i in circles[0, :]:
cv2.circle(img, (i[0], i[1]), i[2], (0, 255, 0), 2) # Draw outer circle
cv2.circle(img, (i[0], i[1]), 2, (0, 0, 255), 3) # Draw inner circle
- Gray to Histogram
import cv2
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
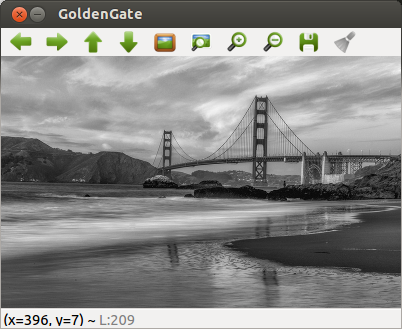
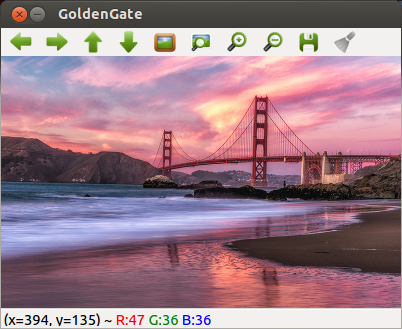
gray_img = cv2.imread('images/GoldenGateSunset.png', cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE)
cv2.imshow('GoldenGate',gray_img)
hist = cv2.calcHist([gray_img],[0],None,[256],[0,256])
plt.hist(gray_img.ravel(),256,[0,256])
plt.title('Histogram for gray scale picture')
plt.show()
 |
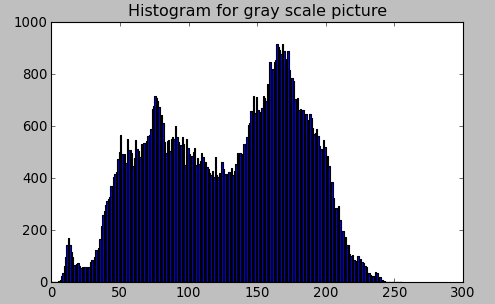 |
- Color to Histogram
import cv2
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
img = cv2.imread('images/GoldenGateSunset.png', -1)
cv2.imshow('GoldenGate',img)
color = ('b','g','r')
for channel,col in enumerate(color):
histr = cv2.calcHist([img],[channel],None,[256],[0,256])
plt.plot(histr,color = col)
plt.xlim([0,256])
plt.title('Histogram for color scale picture')
plt.show()
 |
 |
- Histogram Equalization
python jpg_histogram_equalization.py
img = cv2.imread('test.jpg')
src = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
dst = cv2.equalizeHist(src)
cv2.imshow('Source', src)
cv2.imshow('Equalized', dst)
- Histogram Backprojection
python jpg_histogram_backprojection.py
-
求圖像輪廓 cnts, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(thresh, mode, method)
-
畫輪廓 cv2.drawContours(img, cnts, contourIdx, color, lineType)
-
求包覆矩形 (x,y,w,h) = cv2.boundingRect(cnt)
-
求包覆矩形 box = cv2.minAreaRect(cnt)
-
求包覆圓形 ((x,y), radius) = cv2.minEnclosingCircle(cnt)
-
求包覆橢圓形 ellipse = cv2.fitEllipse(cnt)
-
計算輪廓面積 area = cv2.contourArea(cnt)
-
contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(thresh, mode, method)- img : output image
- contours:包含所有輪廓的容器(vector),每個輪廓都是儲存點的容器(vector),所以contours的資料結構為vector< vector>。
- hierarchy:可有可無的輸出向量,以階層的方式記錄所有輪廓
- thresh:輸入圖,使用八位元單通道圖,所有非零的像素都會列入考慮,通常為二極化後的圖
- mode:取得輪廓的模式
- cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL:只取最外層的輪廓。
- cv2.RETR_LIST:取得所有輪廓,不建立階層(hierarchy)。
- cv2.RETR_CCOMP:取得所有輪廓,儲存成兩層的階層,首階層為物件外圍,第二階層為內部空心部分的輪廓,如果更內部有其餘物件,包含於首階層。
- cv2.RETR_TREE:取得所有輪廓,以全階層的方式儲存。
- method:儲存輪廓點的方法
- cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_NONE:儲存所有輪廓點。
- cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE:對水平、垂直、對角線留下頭尾點,所以假如輪廓為一矩形,只儲存對角的四個頂點。
-
cv2.drawContours(image, contours, contourIdx, color, lineType)- image:輸入輸出圖,會將輪廓畫在此影像上
- contours:包含所有輪廓的容器(vector),也就是findContours()所找到的contours
- contourIdx:指定畫某個輪廓 (-1 = all)
- color:繪製的顏色 (0,0,255) in G-B-R
- lineType:繪製的線條型態
-
Examples:
python jpg_contour_hand.py
img_path = "hand.jpg"
img = cv.imread(img_path)
# define the upper and lower boundaries of the HSV pixel intensities
# to be considered 'skin'
hsvim = cv.cvtColor(img, cv.COLOR_BGR2HSV)
lower = np.array([0, 48, 80], dtype="uint8")
upper = np.array([20, 255, 255], dtype="uint8")
skinMask= cv.inRange(hsvim, lower, upper)
# blur the mask to help remove noise
skinMask= cv.blur(skinMask, (2, 2))
# get threshold image
ret, thresh = cv.threshold(skinMask, 100, 255, cv.THRESH_BINARY)
cv.imshow("thresh", thresh)
# draw the contours on the empty image
contours, hierarchy = cv.findContours(thresh, cv.RETR_TREE, cv.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
contours = max(contours, key=lambda x: cv.contourArea(x))
cv.drawContours(img, [contours], -1, (255, 255, 0), 2)
cv.imshow("contours", img)
cv.waitKey()
pip install cvzone
import cvzone
import cv2
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(0)
cap.set(3, 1280)
cap.set(4, 720)
detector = cvzone.HandDetector(detectionCon=0.5, maxHands=1)
while True:
# Get image frame
success, img = cap.read()
# Find the hand and its landmarks
img = detector.findHands(img)
lmList, bbox = detector.findPosition(img)
# Display
cv2.imshow("Image", img)
cv2.waitKey(1)
python color_matching_histogram.py
python color_matching_meanstddev.py

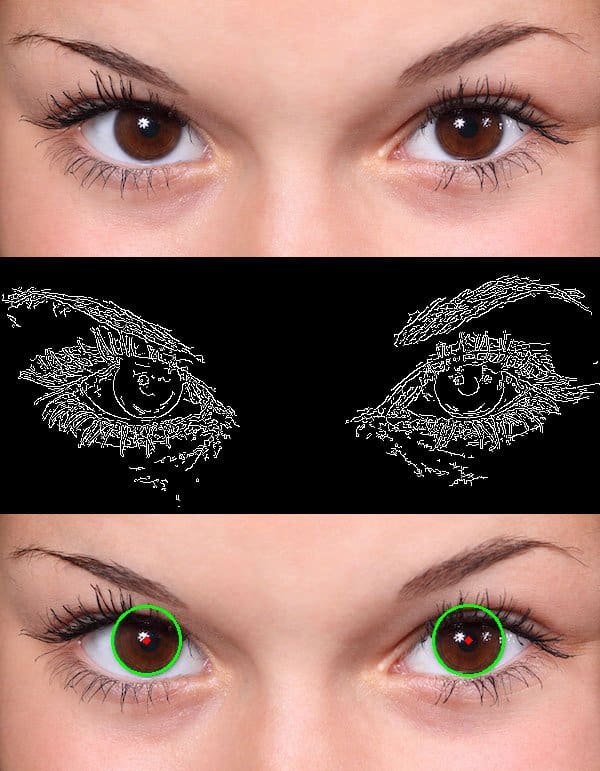
Face Detection using Cascade Classifier
python jpg_face_detect.py
if len(sys.argv)>1:
img = cv2.imread(sys.argv[1])
else:
img = cv2.imread("friends.jpg")
gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
face = cv2.CascadeClassifier('haarcascade_frontalface_default.xml')
bboxes = face.detectMultiScale(gray)
for box in bboxes:
print(box)
(x,y,w,h) = tuple(box)
img = cv2.rectangle(img,(x,y),(x+w,y+h),(255,0,0),2)
cv2.imshow('img',img)
git clone https://github.com/informramiz/opencv-face-recognition-pythoncd opencv-face-recognition-pythonpython3 OpenCV-Face-Recognition-Python.py

Tracker: csrt, kcf, boosting, mil, tld, medianflow, mosse
- csrt for slower FPS, higher object tracking accuracy
- kcf for faster FPS, lower object tracking accuracy
- mosse for fastest FPS
Tracking multiple objects with OpenCV
~/cv2/multi_object_tracking.py
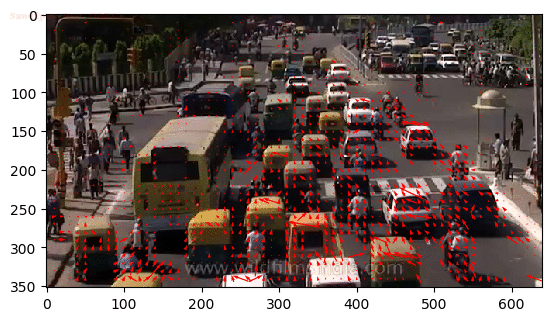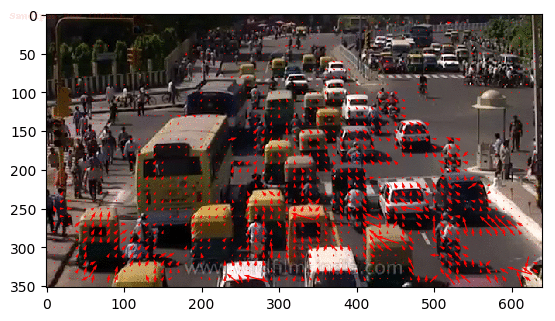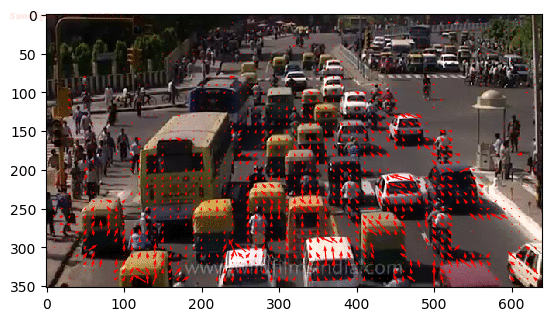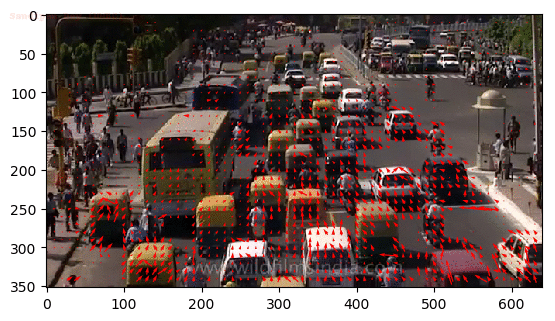
Introduction to Motion Estimation with Optical Flow
The problem of optical flow may be expressed as:
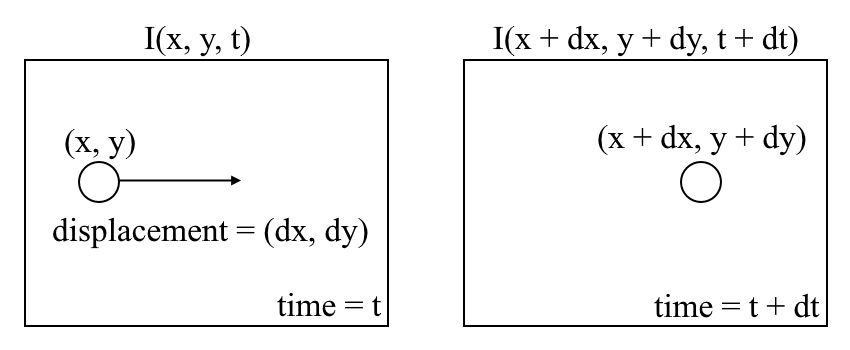
- First, we assume that pixel intensities of an object are constant between consecutive frames.
- Second, we take the Taylor Series Approximation of the RHS and remove common terms.
- Third, we divide by dt to derive the optical flow equation:
where u = dx/dt, v = dy/dt
To track the motion of vehicles across frames
python drone_optical_flow.py
Basic motion detection and tracking with Python and OpenCV
~/cv2/cam_motion_detection.py
git clone https://github.com/thearn/webcam-pulse-detector
cd webcam-pulse-detector
python get_pulse.py
Blog: Real-time Distance Measurement Using Single Image

- Tesseract OCR
- Tesseract Documentation
- Tesseract installers for Windows
Blog: Open OCR and text recognition with Tesseract

Blog: Improve Accuracy of OCR using Image Preprocessing
Scaling Image
python ocr_skew_correction.py
- 安裝函式庫
pip install pyzbar - QR code 產生器:~/cv2/qr_gen.html
- ~/cv2/qr_scan.py
python qr_scan.py -i qr_csu.jpg
cadenCV is an optical music recognition system written in the Python programming language which reads sheet music and sequences a MIDI file for user playback.
git clone https://github.com/afikanyati/cadenCV
cd cadenCV
rm output/*
pip install midiutil
python main.py resources/samples/mary.jpg
Output: .jpg & .midi
- html-midi player : upload output.mid & play